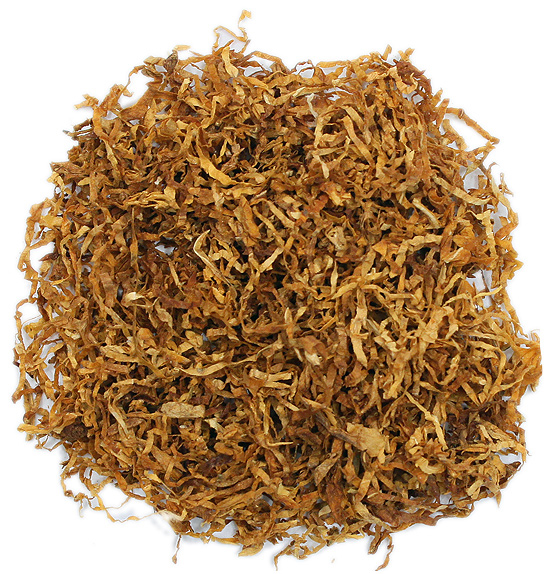
Recently I realized with a shock that I had never written a proper blogpost about an essential tobacco process: curing. Ok, here and there in older blogposts I told stuff but nothing combined. So I put all the bits and pieces together with some additional info. The primary purpose of curing leaf tobacco is to accelerate the ageing and drying processes under controlled conditions to make it ready for consumption. Trust me, you do not want to smoke fresh tobacco.. Curing allows for the slow oxidation and degradation of carotenoids in the tobacco leaf. This produces various compounds that give cured tobacco the “smoothness” of the consumed end-product. The primary methods of curing include: air curing, flue curing, fire curing (or smoke curing) and sun curing (considered by some people to be the same as air curing).
Recently I realized with a shock that I had never written a proper blogpost about an essential tobacco process: curing. Ok, here and there in older blogposts I told stuff but nothing combined. So I put all the bits and pieces together with some additional info. The primary purpose of curing leaf tobacco is to accelerate the ageing and drying processes under controlled conditions to make it ready for consumption. Trust me, you do not want to smoke fresh tobacco.. Curing allows for the slow oxidation and degradation of carotenoids in the tobacco leaf. This produces various compounds that give cured tobacco the “smoothness” of the consumed end-product. The primary methods of curing include: air curing, flue curing, fire curing (or smoke curing) and sun curing (considered by some people to be the same as air curing).
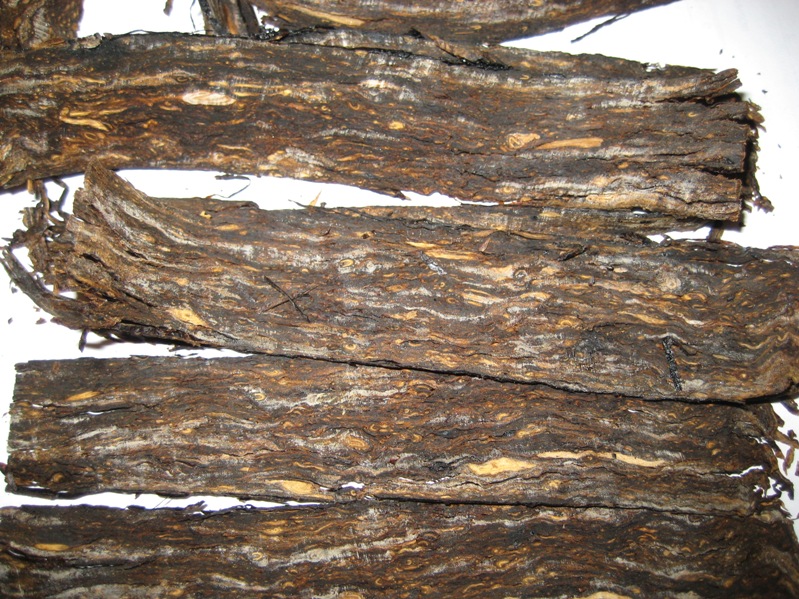
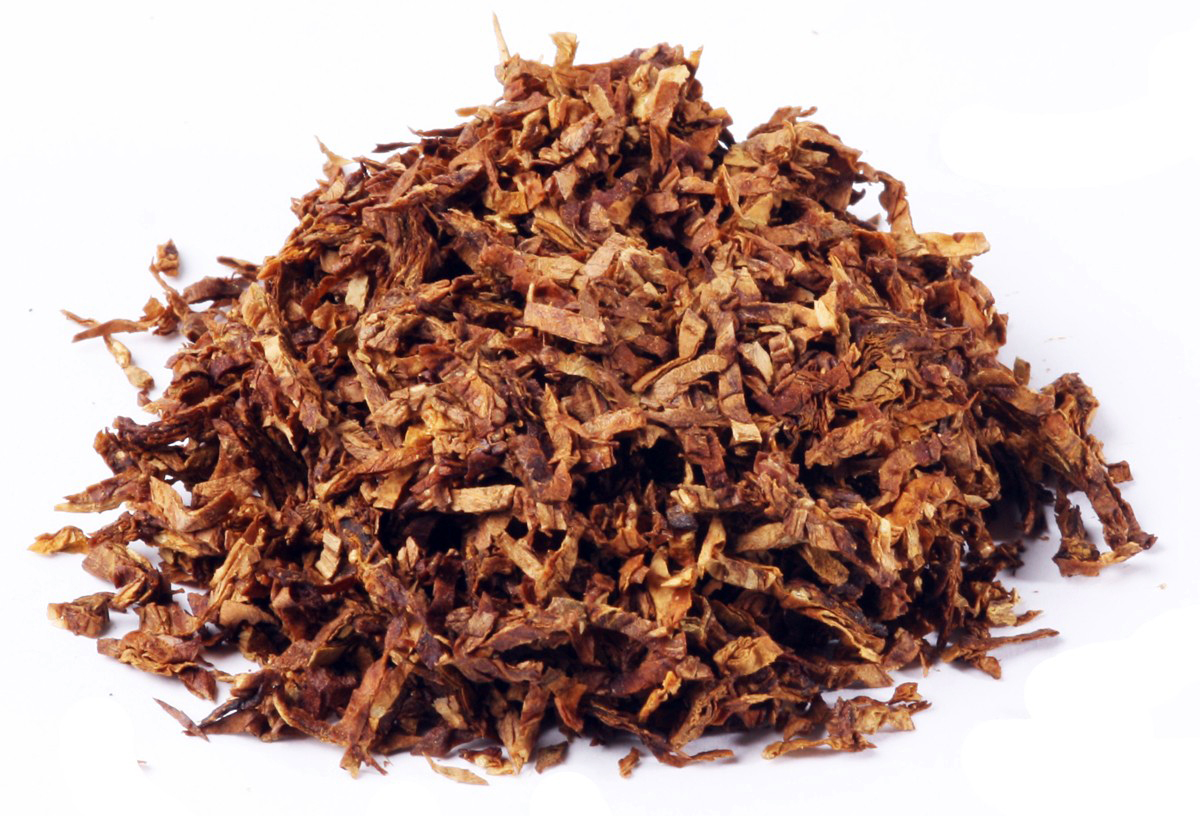
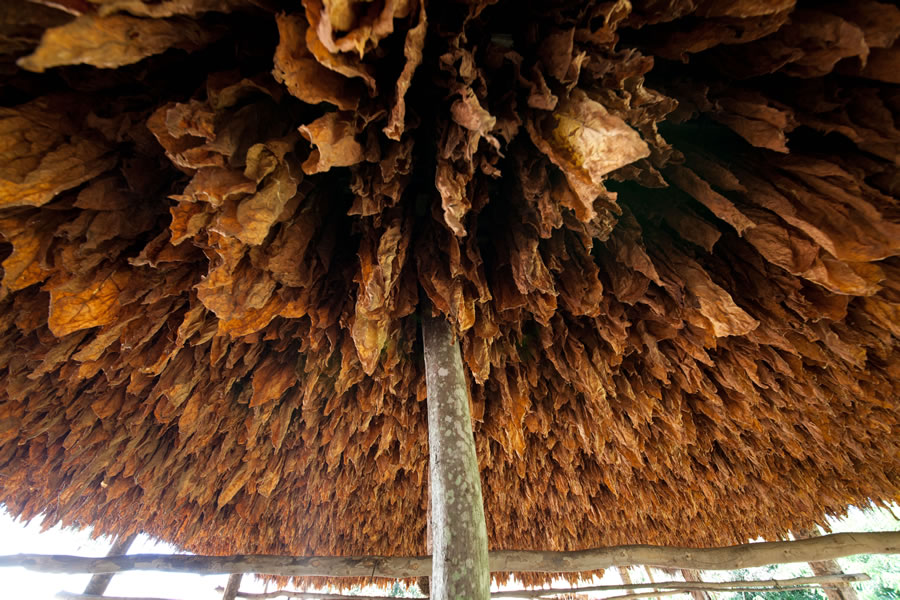 Air curing: here the leaves are allowed to dry by exposure to air in well ventilated barns. Fans can also be used in this process to make the air movement stronger to accelerate the loss of moisture. This air curing process normally takes from 4 to 6 weeks. It is completed when the central vein of the leaf is completely free of sap. This type of curing is used primarily for burley. Light air cured burley and dark air cured burley to be precise. The top grades of light air cured burley, which are yellow, are referred to as “White Burley”. These larger, thinner middle leaves are those most desired for the manufacture of fine pipe tobacco and premium quality cigarettes. White burley has a fine texture, excellent burning qualities and the ability to absorb large amounts of casings and flavourings. The top and bottom leaves are used in the manufacture of snuff, plugs, twist and inexpensive brands of pipe smoking tobacco. The taste is nutty, sometimes with a bit of a cocoa note.
Air curing: here the leaves are allowed to dry by exposure to air in well ventilated barns. Fans can also be used in this process to make the air movement stronger to accelerate the loss of moisture. This air curing process normally takes from 4 to 6 weeks. It is completed when the central vein of the leaf is completely free of sap. This type of curing is used primarily for burley. Light air cured burley and dark air cured burley to be precise. The top grades of light air cured burley, which are yellow, are referred to as “White Burley”. These larger, thinner middle leaves are those most desired for the manufacture of fine pipe tobacco and premium quality cigarettes. White burley has a fine texture, excellent burning qualities and the ability to absorb large amounts of casings and flavourings. The top and bottom leaves are used in the manufacture of snuff, plugs, twist and inexpensive brands of pipe smoking tobacco. The taste is nutty, sometimes with a bit of a cocoa note.
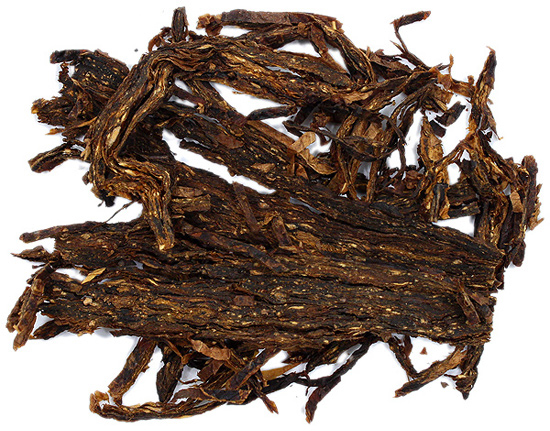
 Dark Air cured burley is mostly used for chewing tobacco, plugs, snuff and inexpensive brands of pipe tobacco. The lower grades (or heavier leaves) are used in some tobacco mixtures to give the tobacco blend more “body”. The taste is earthy, spicy and cigar-like and the colour of the leaves ranges from light to dark brown. Most cigar leaf is also air cured but will undergo an extra step: “bulking”. Essentially this means that big bundles are made of the leaves so that they can be laid to rest in order to start the fermentation process. The pepperiness of burley and many of the Central American-grown Cuban-seed cigar strains comes from the nicotine that naturally is in the leaf.
Dark Air cured burley is mostly used for chewing tobacco, plugs, snuff and inexpensive brands of pipe tobacco. The lower grades (or heavier leaves) are used in some tobacco mixtures to give the tobacco blend more “body”. The taste is earthy, spicy and cigar-like and the colour of the leaves ranges from light to dark brown. Most cigar leaf is also air cured but will undergo an extra step: “bulking”. Essentially this means that big bundles are made of the leaves so that they can be laid to rest in order to start the fermentation process. The pepperiness of burley and many of the Central American-grown Cuban-seed cigar strains comes from the nicotine that naturally is in the leaf.
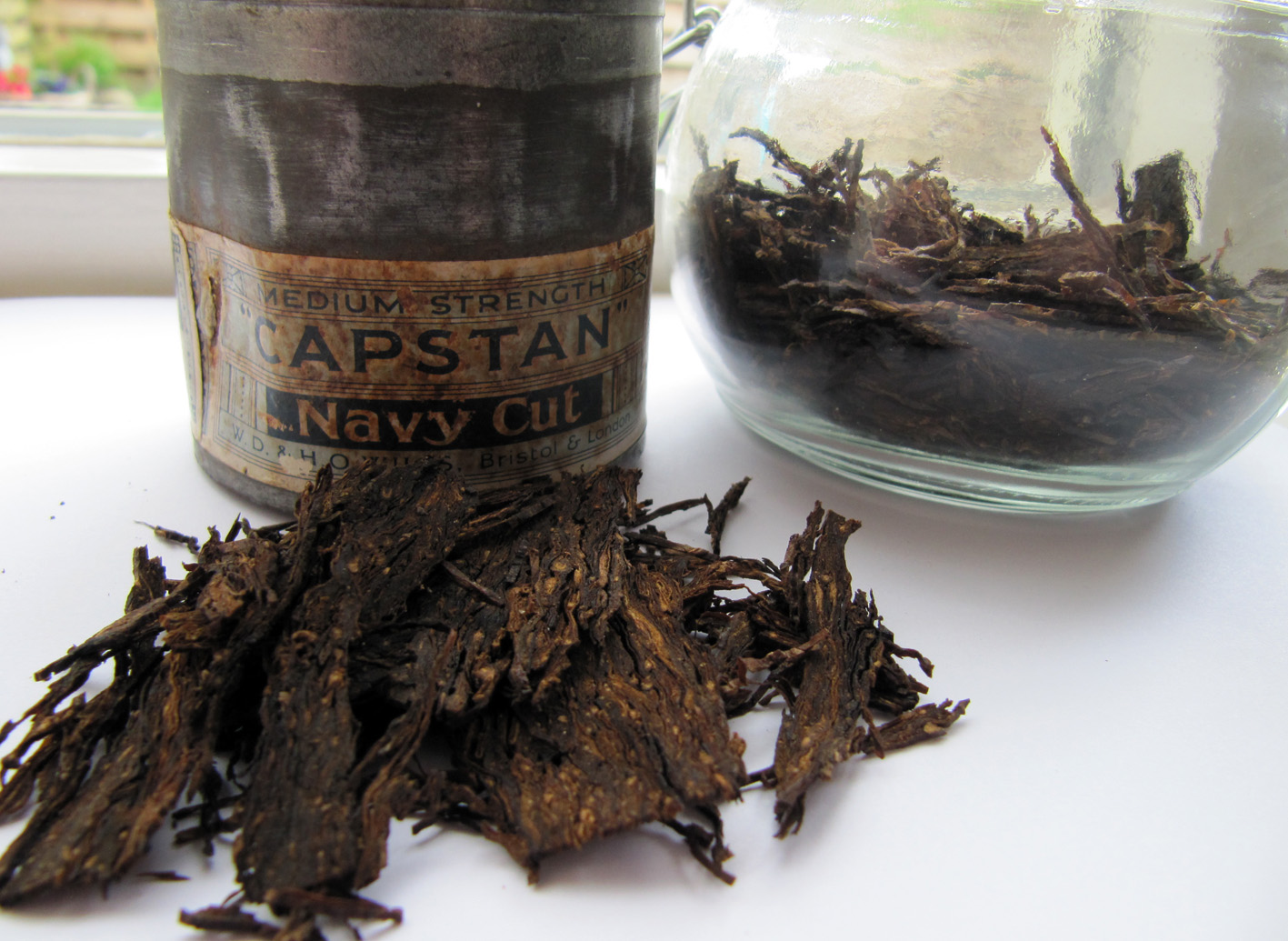
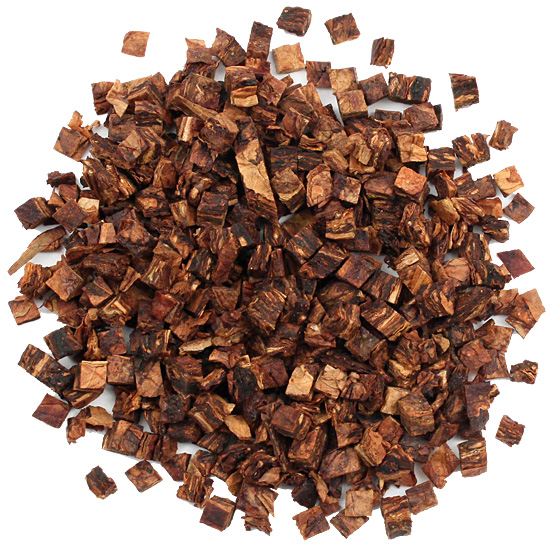
 Fire curing (or smoke curing): here the leaves are essentially BBQed. In the case of dark fired Kentucky burley they are exposed to open fires (smouldering, not blazing, otherwise the tobacco will prematurely burn up) of hardwood and hardwood sawdust that are maintained on the barn-floor and give off smoke. In some cases, the amount of smoke is fairly moderate. In addition to drying the tobacco the fire curing process imparts an unusual, modest smoky and wood-like taste and aroma to the tobacco. Latakia is also a fire cured tobacco but has a far more pronounced smoke flavour and aroma. This is due to the intensity of the fumes and aromatic quality of the used woods. Syrian latakia is derived from a tobacco leaf known as “shekk-el-bint.” When it is harvest time the plant is cut and the leaves and flowers are laid on the ground to dry in the sun (essentially sun curing). When they have dried they are taken to storehouses, where they are smoked for a period of 13 to 15 weeks. The smoke is primarily made by using nearby hardwoods and pines, probably from the Baer forest, such as Aleppo pine, Turkey oak and Valonia oak. Also lesser amounts of other aromatic species like Lebanon cedar and Greek Juniper were used.
Fire curing (or smoke curing): here the leaves are essentially BBQed. In the case of dark fired Kentucky burley they are exposed to open fires (smouldering, not blazing, otherwise the tobacco will prematurely burn up) of hardwood and hardwood sawdust that are maintained on the barn-floor and give off smoke. In some cases, the amount of smoke is fairly moderate. In addition to drying the tobacco the fire curing process imparts an unusual, modest smoky and wood-like taste and aroma to the tobacco. Latakia is also a fire cured tobacco but has a far more pronounced smoke flavour and aroma. This is due to the intensity of the fumes and aromatic quality of the used woods. Syrian latakia is derived from a tobacco leaf known as “shekk-el-bint.” When it is harvest time the plant is cut and the leaves and flowers are laid on the ground to dry in the sun (essentially sun curing). When they have dried they are taken to storehouses, where they are smoked for a period of 13 to 15 weeks. The smoke is primarily made by using nearby hardwoods and pines, probably from the Baer forest, such as Aleppo pine, Turkey oak and Valonia oak. Also lesser amounts of other aromatic species like Lebanon cedar and Greek Juniper were used.
 Cyprian latakia comes from a Smyrna or Izmir-type tobacco plant that is known as “Yellow Cyprus.” The Yellow Cyprus leaves are harvested by de-stalking them and are made on long poles to be hung in a tobacco shed. The leaves are then smoked over open smouldering fires. These fires are made from hardwoods, some pine and aromatic shrubs and woods such as prickly cedar and myrtle. It has been reported that the Mastic shrub is primarily used in the smoke generation for Cyprian latakia. The following formula may approximate the shrubs and woods used for the fire/smoke-curing process: Mastic 90%, Myrtle 4%, Stone pine (this one or this one) 4%, Cypress 1%, Other 1%. The nicotine content does not seem to be severely affected by the process. Dark fired Kentucky burley with its significant nicotine level is not that much different from the dark air cured variety. The moderate nicotine level of latakia does not vary greatly from the oriental base leaf it is made of.
Cyprian latakia comes from a Smyrna or Izmir-type tobacco plant that is known as “Yellow Cyprus.” The Yellow Cyprus leaves are harvested by de-stalking them and are made on long poles to be hung in a tobacco shed. The leaves are then smoked over open smouldering fires. These fires are made from hardwoods, some pine and aromatic shrubs and woods such as prickly cedar and myrtle. It has been reported that the Mastic shrub is primarily used in the smoke generation for Cyprian latakia. The following formula may approximate the shrubs and woods used for the fire/smoke-curing process: Mastic 90%, Myrtle 4%, Stone pine (this one or this one) 4%, Cypress 1%, Other 1%. The nicotine content does not seem to be severely affected by the process. Dark fired Kentucky burley with its significant nicotine level is not that much different from the dark air cured variety. The moderate nicotine level of latakia does not vary greatly from the oriental base leaf it is made of.
 Flue curing: here the leaves are cured by exposure to indirect heat. This is created by moving hot air, smoke or steam through a flue or pipe inside a building (often a barn) thus allowing the heat to strongly warm up the building. The higher heat causes a more rapid drying effect and is the traditional method for curing Virginia. The yellow colour you often see Virginia has comes from the heat exposure. Generally the process will take about a week. This way of flue curing was not discovered until 1839. In that year a slave, Stephen Slade (owned by farmer Abisha Slade from Caswell County NC), fell asleep one night while keeping an eye on the wood fires used for curing the barns of tobacco. Whether it was the stormy night, instinct or just what woke him, no one will ever know. But he awoke realizing that the fires in the tobacco curing barn had almost gone out. Rather than throw wet wood into the dying fire, he rushed to the charcoal pit near the forge. He grabbed several charred log parts and threw them on the embers. The application of the sudden, drying heat, derived from the charred logs, produced an amazing effect on the green tobacco. The result was 600 pounds of the brightest yellow tobacco ever seen.
Flue curing: here the leaves are cured by exposure to indirect heat. This is created by moving hot air, smoke or steam through a flue or pipe inside a building (often a barn) thus allowing the heat to strongly warm up the building. The higher heat causes a more rapid drying effect and is the traditional method for curing Virginia. The yellow colour you often see Virginia has comes from the heat exposure. Generally the process will take about a week. This way of flue curing was not discovered until 1839. In that year a slave, Stephen Slade (owned by farmer Abisha Slade from Caswell County NC), fell asleep one night while keeping an eye on the wood fires used for curing the barns of tobacco. Whether it was the stormy night, instinct or just what woke him, no one will ever know. But he awoke realizing that the fires in the tobacco curing barn had almost gone out. Rather than throw wet wood into the dying fire, he rushed to the charcoal pit near the forge. He grabbed several charred log parts and threw them on the embers. The application of the sudden, drying heat, derived from the charred logs, produced an amazing effect on the green tobacco. The result was 600 pounds of the brightest yellow tobacco ever seen.
 Flue cured tobacco generally has more sugar, less oil and a lower nicotine content. The presence of the sugar counters tongue bite but can cause heat issues while smoking. Naturally sugars tend to have a higher combustion temperature. Because of the ability of this curing method to maintain the sugars in a relatively stable percentage a form of flue curing is used in making candela cigar wrapper. The heat not only fixes the few sugars present but the chlorophyll as well thus allowing the wrappers to stay green.
Flue cured tobacco generally has more sugar, less oil and a lower nicotine content. The presence of the sugar counters tongue bite but can cause heat issues while smoking. Naturally sugars tend to have a higher combustion temperature. Because of the ability of this curing method to maintain the sugars in a relatively stable percentage a form of flue curing is used in making candela cigar wrapper. The heat not only fixes the few sugars present but the chlorophyll as well thus allowing the wrappers to stay green.
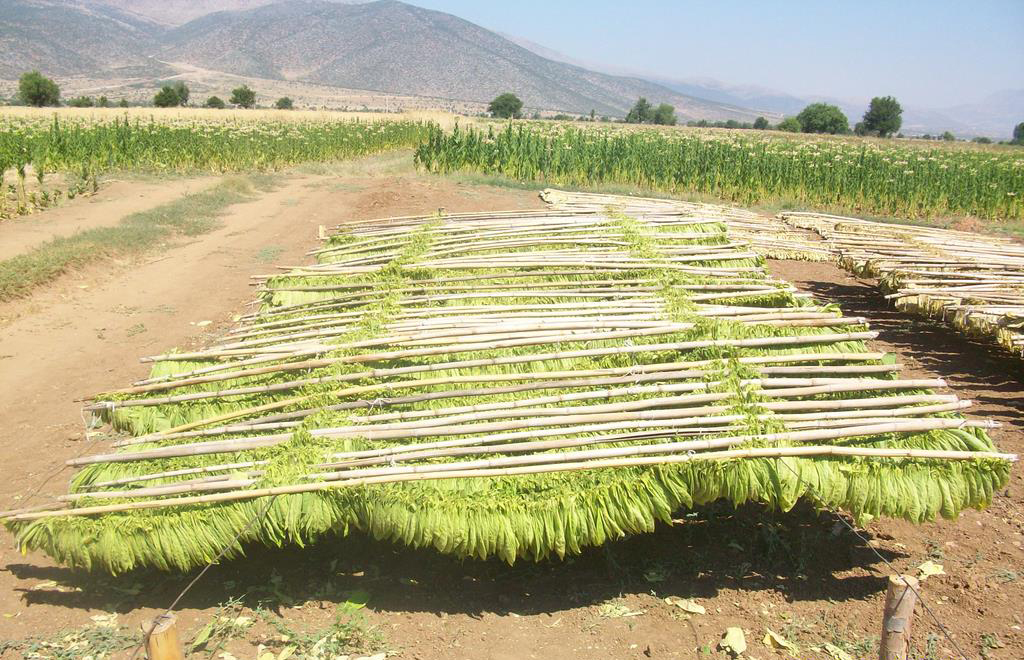 Sun curing: this method is used in Turkey, Greece, Bulgaria, Macedonia, Romania and Mediterranean countries which produce oriental tobaccos. Leaves are strung out on racks and exposed to the sun for 12 to 30 days to remove most of their moisture before being air cured to complete the process. The sun’s direct heat fixes the leaves at a yellow to orange colour with a high sugar content. Then they are stored in bales and allowed to ferment.
Sun curing: this method is used in Turkey, Greece, Bulgaria, Macedonia, Romania and Mediterranean countries which produce oriental tobaccos. Leaves are strung out on racks and exposed to the sun for 12 to 30 days to remove most of their moisture before being air cured to complete the process. The sun’s direct heat fixes the leaves at a yellow to orange colour with a high sugar content. Then they are stored in bales and allowed to ferment.
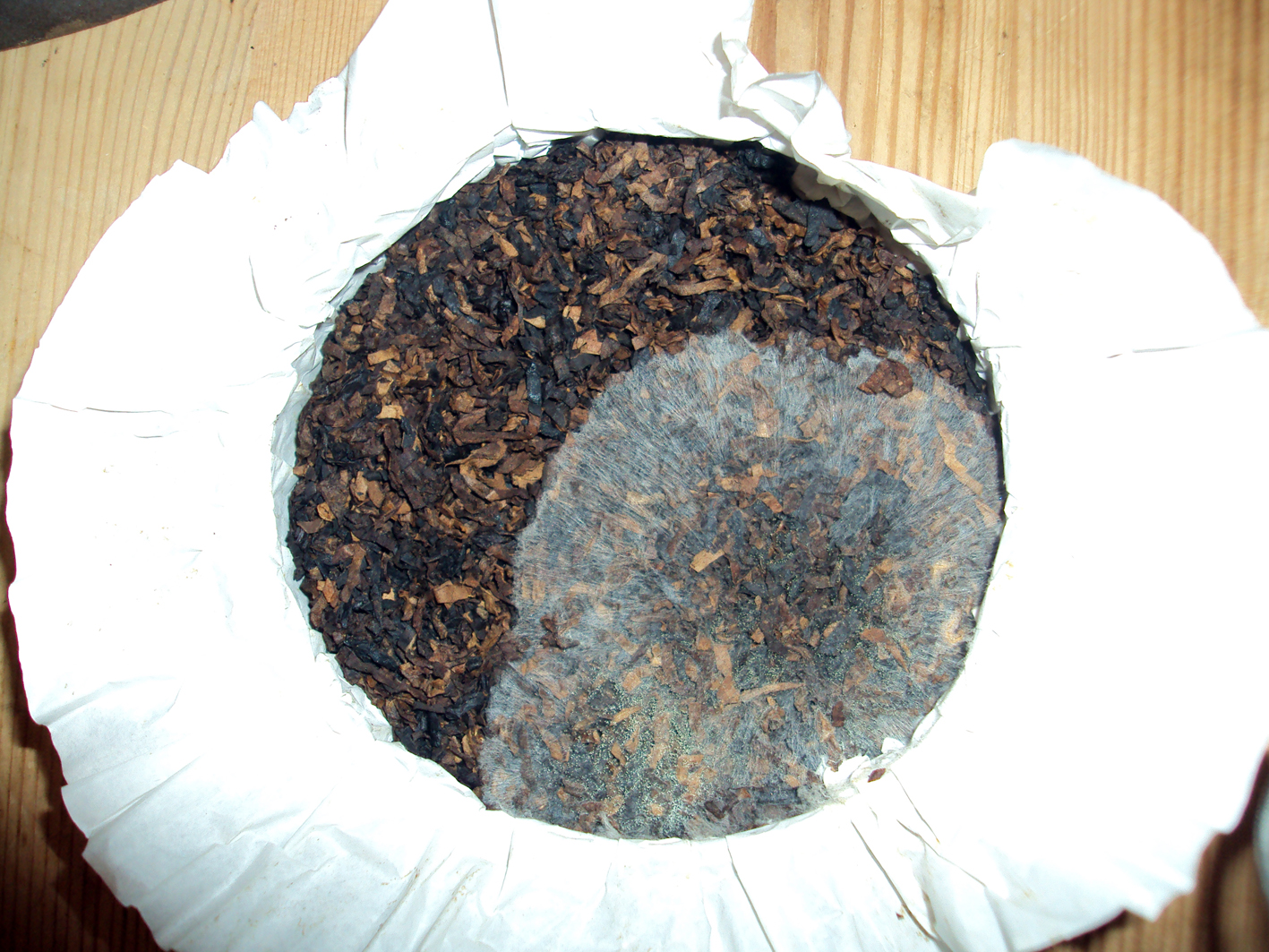
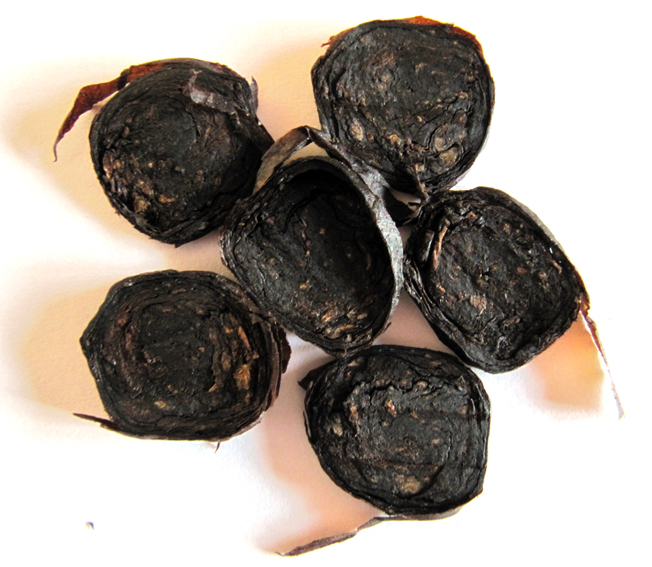
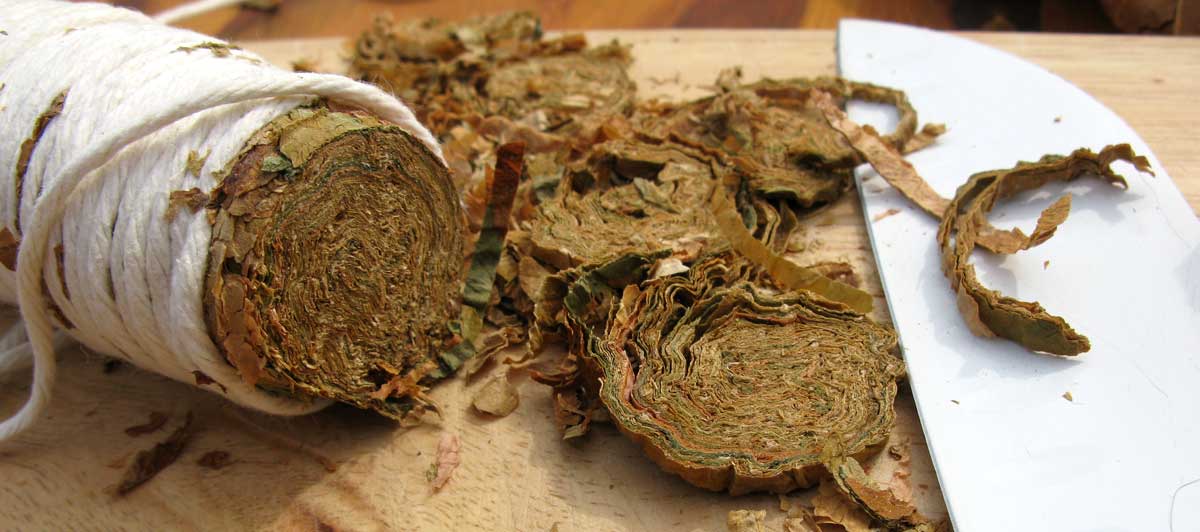
Additional or supplementary curing can be done by the use of heat and/or pressure after the initial process. A good example of pressure is the technique of pressure-fermentation which is used in making perique. This process remains a traditional craft, not much has changed since the early 20th century. First air cured tobacco is hand stripped. The leaf which is used is considered to be pretty similar to burley. The only moisture added is just prior to the stripping to make the leaves pliable. How many moisture is used is up to the craftsmen. You just have to feel it. Then the tobacco is rolled into “torquettes” of approximately 1 pound (450 g) and packed into hickory whisky barrels. These are topped off with a wooden lid and pressed by using oak blocks and massive screw jacks. Thus forcing nearly all the air out of the still moist leaves. The barrels are unpacked at least three times during the active fermentation phase (around five months). The torquettes are then repacked in the barrels in reverse order (former top bundles on bottom and bottom bundles on top) to permit a little air back into the tobacco. They are then closely monitored with periodic increases of pressure. After at least a year of this treatment, the perique is ready for consumption.
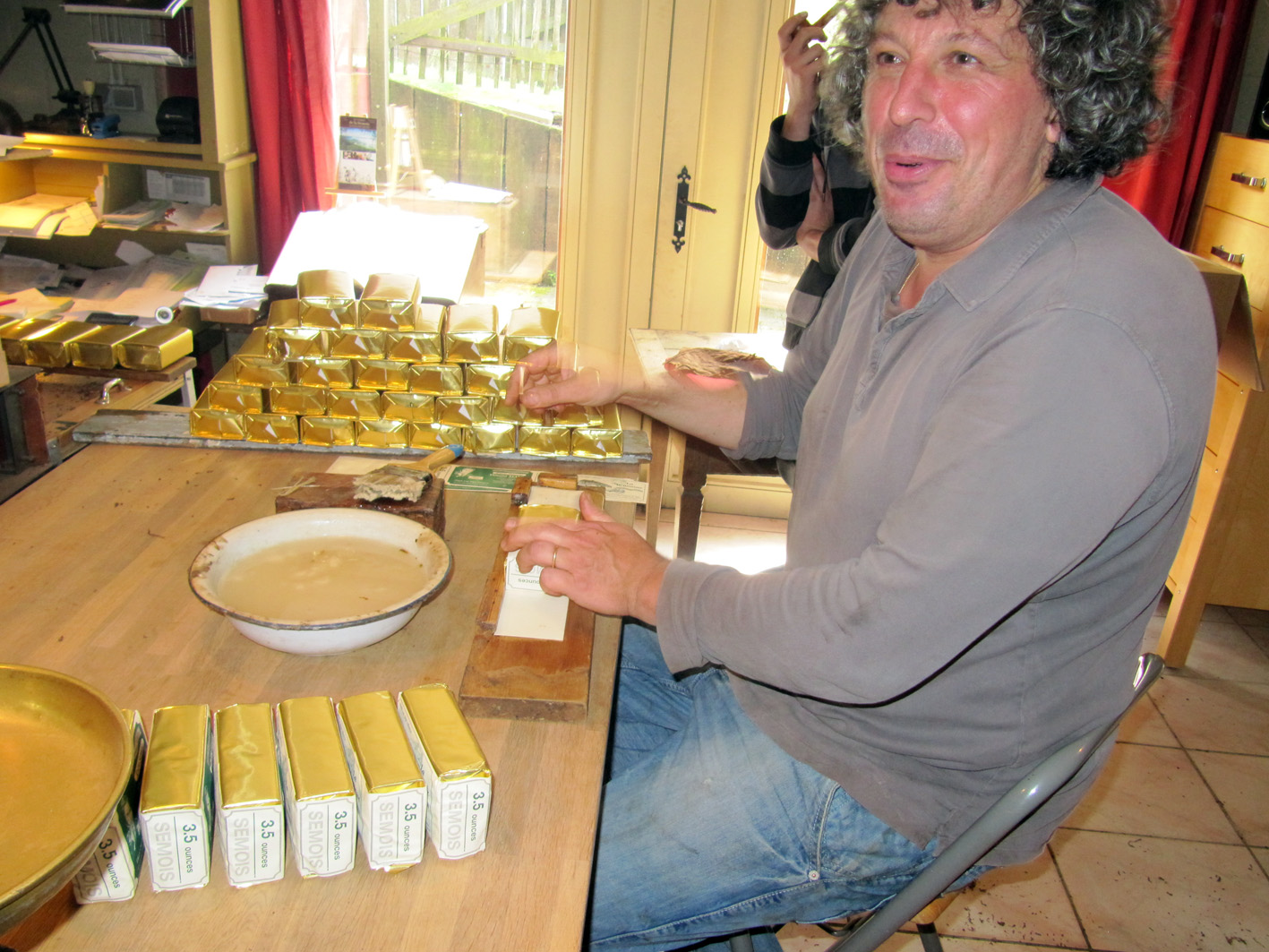
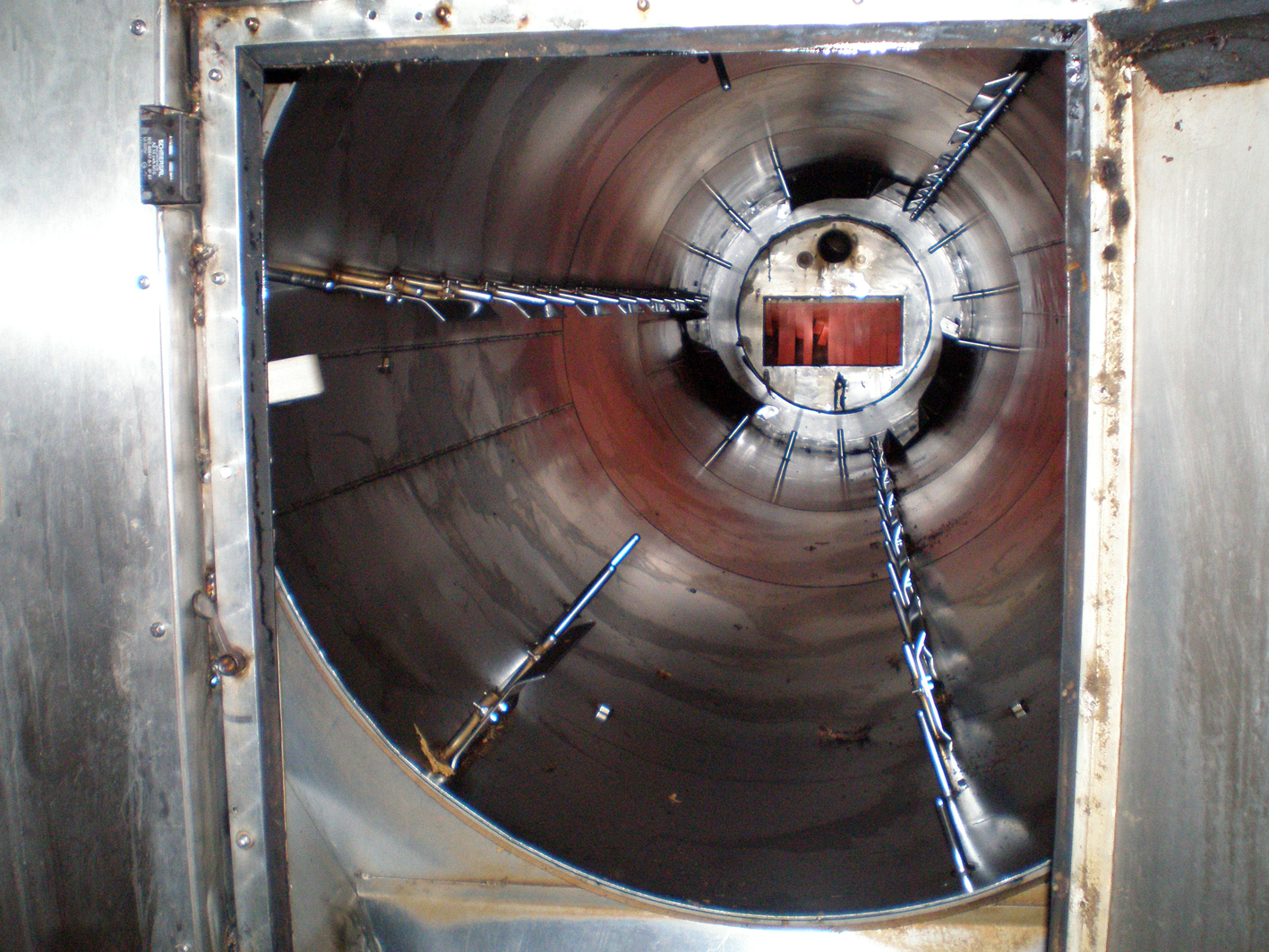
 A good example of supplementary curing by the use of heat is the fascinating Belgian leaf, Semois. First it is air cured (after all Semois is a type of burley) and then it is sort of heat cured. This because the tobacco is toasted in what looks like a metal custom made wood-burning oven. Inside is a large drum which is heated by a fire below and can spin around. The tobacco is put inside and while tumbling it is getting toasted.
A good example of supplementary curing by the use of heat is the fascinating Belgian leaf, Semois. First it is air cured (after all Semois is a type of burley) and then it is sort of heat cured. This because the tobacco is toasted in what looks like a metal custom made wood-burning oven. Inside is a large drum which is heated by a fire below and can spin around. The tobacco is put inside and while tumbling it is getting toasted.
Th-th-th-that’s all folks!