This year the destination for the summer holiday of Ellen and myself was Germany. Instead of staying in one location we opted to make a week-long trip from the North of Germany, Lübeck, to the Middle-East part; the Ahrtal. In between those two locations we resided in hotels and B&B’s. Of course I planned to visit several tobacco-shops and even a tobacco-factory: DTM in Lauenburg, situated on the northern bank of the river Elbe, east of Hamburg. Lauenburg is just a lovely old town with a picturesque historic centre alongside the Elbe. Small, enchanting streets up the hill lead to what is left of the once mighty Lauenburg castle. Also the view from there is stunning, you cannot only see the beautiful river Elbe and the old town, but also the flat marshland of Lower-Saxony. Lauenburg has one café/restaurant where you can smoke inside: the Alten Schifferhaus, where I left Ellen so I could visit DTM without her beautiful but prying eyes.
First of all, there are 2 separate business entities: Dan Pipe and Dan Tobacco Manufacturing (DTM). Dan Pipe is a retail and catalogue company. Dan Tobacco is a tobacco production facility. The history of Dan Pipe began in 1972 when, after a holiday in Denmark, teacher and enthusiastic pipe smoker Heiko Behrens decided to sell the creations of then unknown Danish pipe makers. In a small catalogue handmade pipes by Former, Emil Chonowitsch and Poul Hansen were presented together with factory pipes from Tabago, Torben Dansk, Danmore and other Danish producers. Soon also pipe tobacco was added to the catalogue, including Dan Pipe‘s first own-brand Torben Dansk. The quality of the pipes and tobaccos from the Dan Pipe catalogue provided good word-of-mouth advertising amongst the German pipe-smokers so gradually the customer base grew.
By 1976 the business was growing so rapidly that a new location was necessary. Behrens contracted craftsman (and aspiring young dentist) Holger Frickert to construct and design a showroom. Frickert was leading a class in art and design and that class rebuilt the shop in the form of a boat. It was an extraordinary design, with sails atop the room. Sadly I could not find any pictures of it.. Frickert’s passion for handicrafts, smoking and pipes led him to abandon dentistry and join Behrens’ business in 1978. He began repairing pipes as well as designing his own plus he became responsible for the catalogue presentation. The company was renamed for legal reasons in “Danske Pibe“.
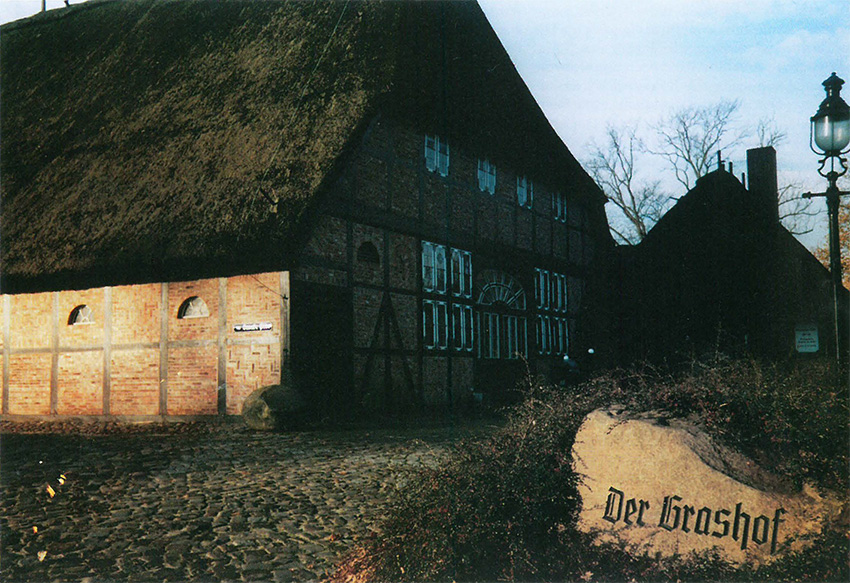
In 1985 Danske Pibe had grew so large that a much more spacious home had to be found. The “Grashof”, a large farmhouse with thatched roof from the 18th century offered ideal conditions. There was space in abundance and on top of that the in 1987 lovingly restored old house, which also housed the store, had a special rustic charm. Over the years it became a “magnetic pole in the north” for tobacco and pipe enthusiasts from all parts of Germany and the surrounding countries. Since the beginning of the 1980’s one of the specialities of the company were the house-brand tobaccos, which soon covered a wide range of flavours. But quality and delivery problems became a threat so decisive action was necessary. A new supplier who was able to cover the entire range of house-brand tobaccos was not in sight. Because of that the decision was made by Danske Pibe to establish their own tobacco factory. In 1991 a suitable building was found in Lauenburg and that was the beginning of subsidiary Dan Tobacco Manufacturing. Simultaneously the parent company returned to its old name Dan Pipe.
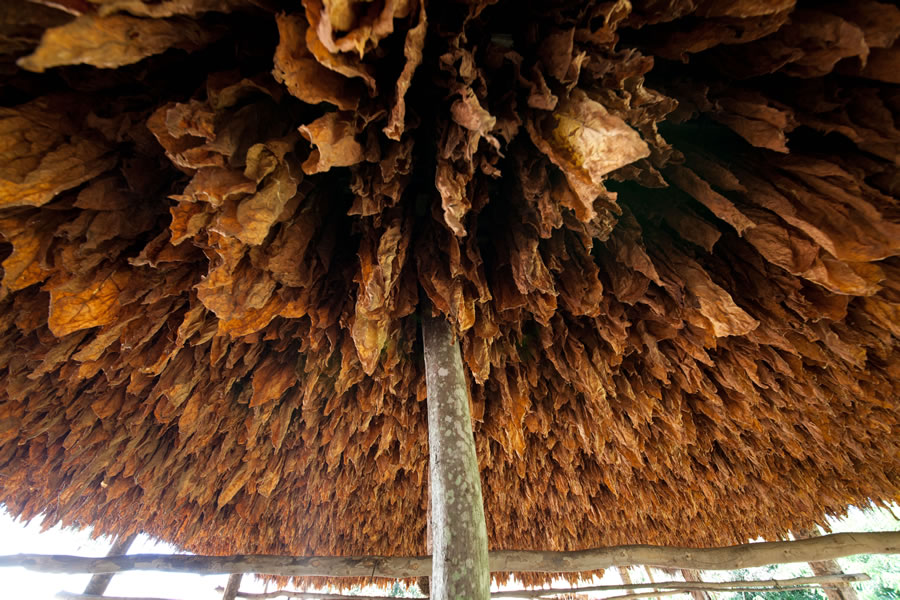
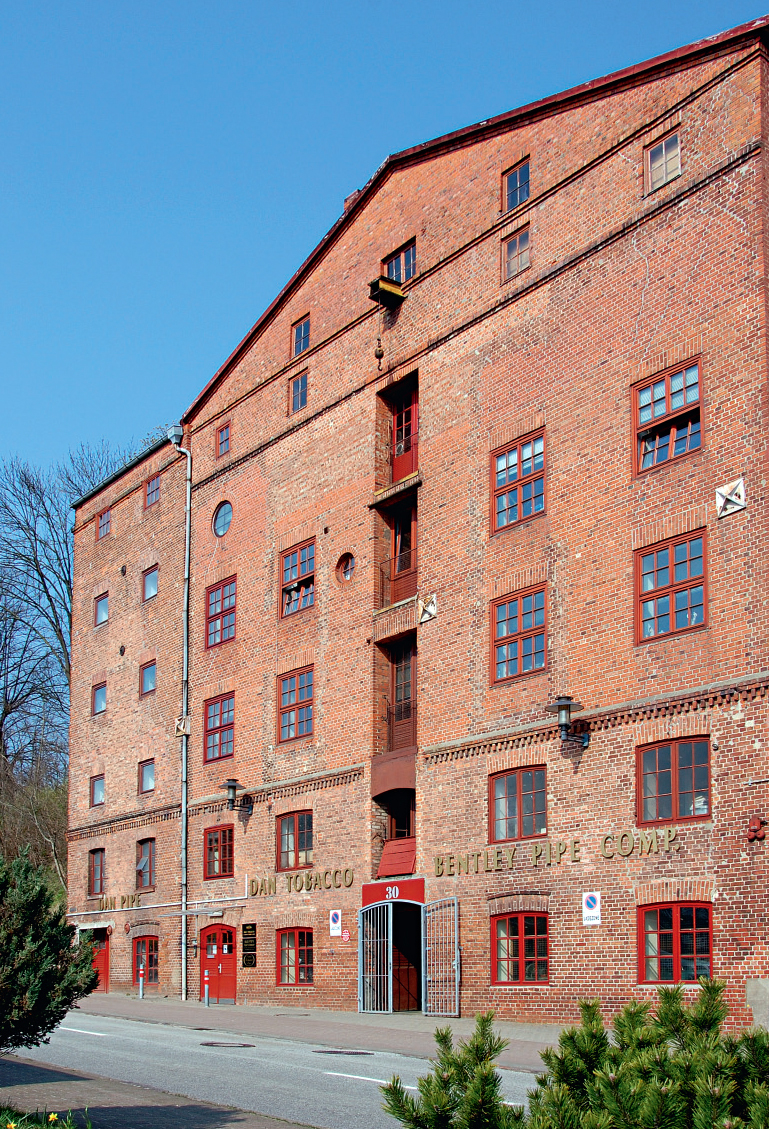 The DTM building is kind of special. It is an old former grain malting house, built of red brick into the steep slope of the Elbe river banks more than 100 years ago with a construction solid like an ancient castle. Enclosed by anywhere from several feet to several hundred feet of rock, the temperature and humidity in it varies no more than 2,5%. The ideal place for storing and producing pipe tobacco. The inevitable start-up problems were soon overcome and thanks to the creativity and experience of the employees of both companies they succeeded in a remarkably short time to generate a sizeable range of tobacco products. Those tobaccos were of such excellent quality that they gained a high international reputation. Thus exports to, for example, USA, Italy, Russia and Japan followed.
The DTM building is kind of special. It is an old former grain malting house, built of red brick into the steep slope of the Elbe river banks more than 100 years ago with a construction solid like an ancient castle. Enclosed by anywhere from several feet to several hundred feet of rock, the temperature and humidity in it varies no more than 2,5%. The ideal place for storing and producing pipe tobacco. The inevitable start-up problems were soon overcome and thanks to the creativity and experience of the employees of both companies they succeeded in a remarkably short time to generate a sizeable range of tobacco products. Those tobaccos were of such excellent quality that they gained a high international reputation. Thus exports to, for example, USA, Italy, Russia and Japan followed.
In 1994 Dan Pipe acquired 4 stores of the Pfeifen Timm chain in Hamburg’s city centre, a pipe-specialist well-known throughout Germany. Thus, the tobacco assortment now included many Timm house-brands. Even a fresh wind went through the cigar assortment and it was greatly increased. Sadly in November 2001 a fire laid the Grashof in ruins. Luckily in Lauenburg at DTM enough space was available, so it became the new home of Dan Pipe. The years during and after the financial crisis were difficult. The shops in Hamburg suffered losses and had to be closed. Dr. Heiko Behrens realised he needed help and so Maria Sousa became the other director. New sources of income had to be found in which the company succeed. Nowadays besides pipe-tobacco, high class water-pipe tobacco is made in Lauenburg.
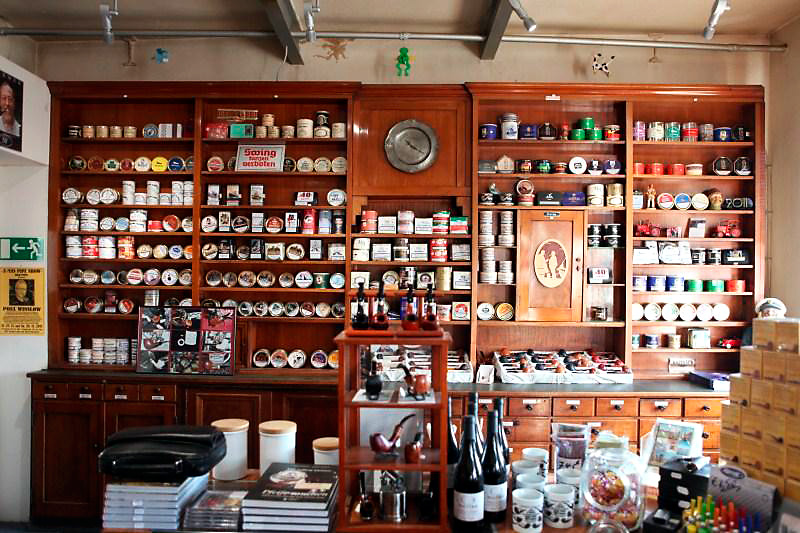
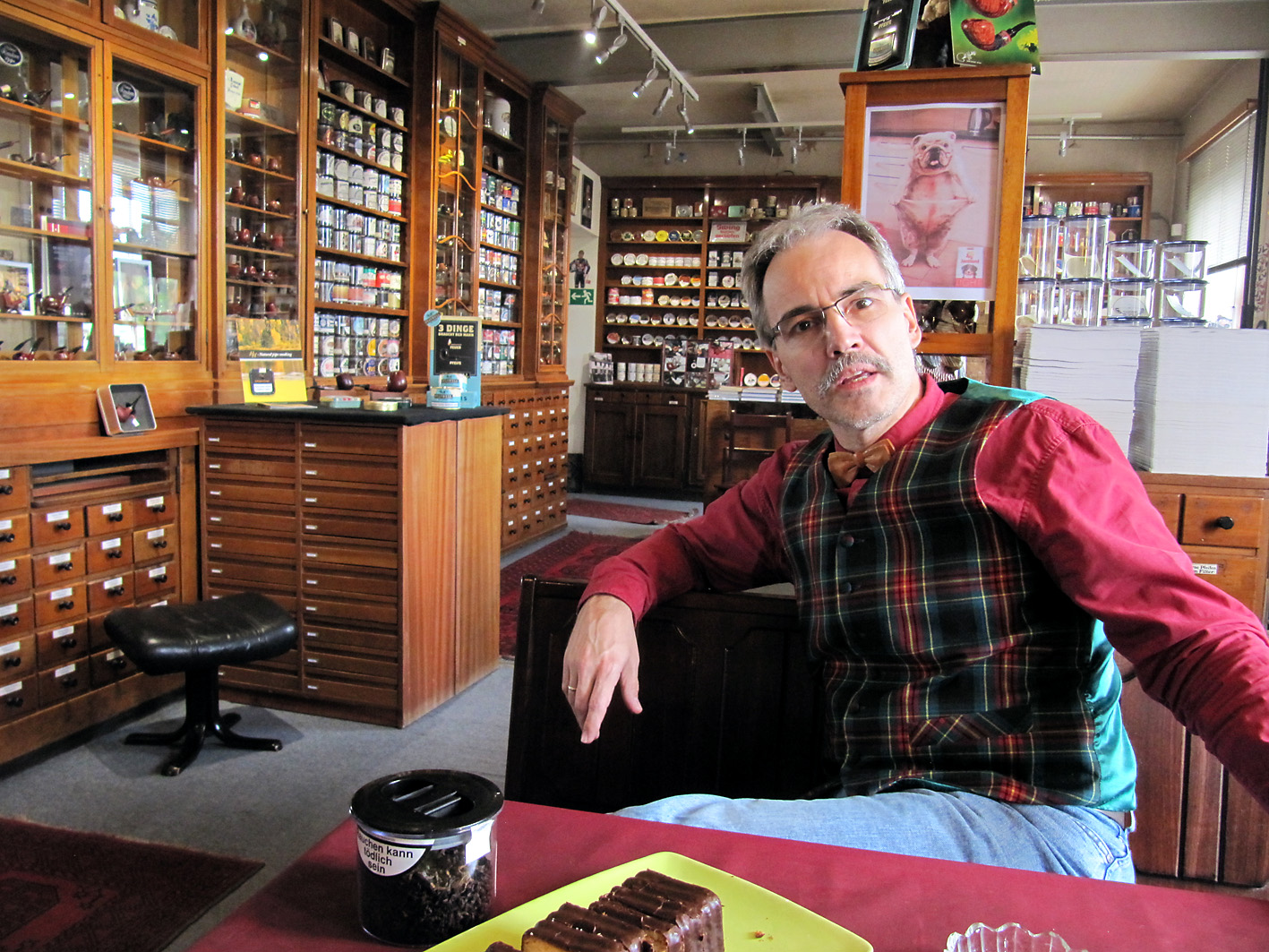
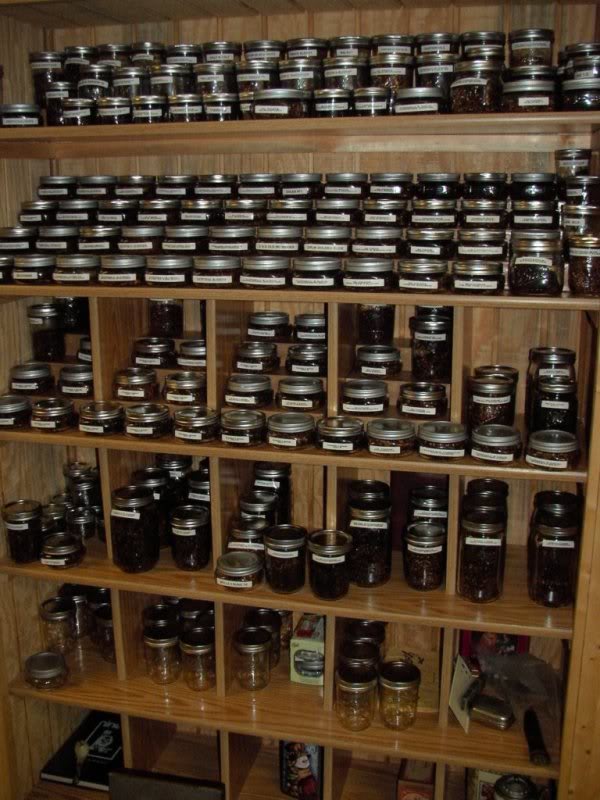
I visited Dan Pipe / DTM several times now. But the first time (like so many things) was special. In 2012 I was busy with the quest for forum tobaccos. It was arranged that good friend and chauffeur Ed and myself would stay there for two days and visit the DTM factory. When we arrived we immediately noticed the sweet smell coming from the building. Someone was making a batch of aromatic tobacco for sure! Inside the Dan Pipe store shop assistant Ralph Kaschwich looked at us a bit questioning. “You come here for two days? Netherlands? Forum tobaccos? Let me make a phone call..” After a brief conversation things were cleared out and we were asked to wait for Andreas Mund, the master blender. That waiting certainly was not a punishment! The store has a beautiful interior from 1920 which is made from solid mahogany and comes from an old Hamburg pharmacy. It has many drawers and shelves where besides pipes about 140 DTM tobaccos are displayed in sample-jars. There also is a table with a bench where you can quietly sit, have a drink, take a piece of cake and (of course) smoke.
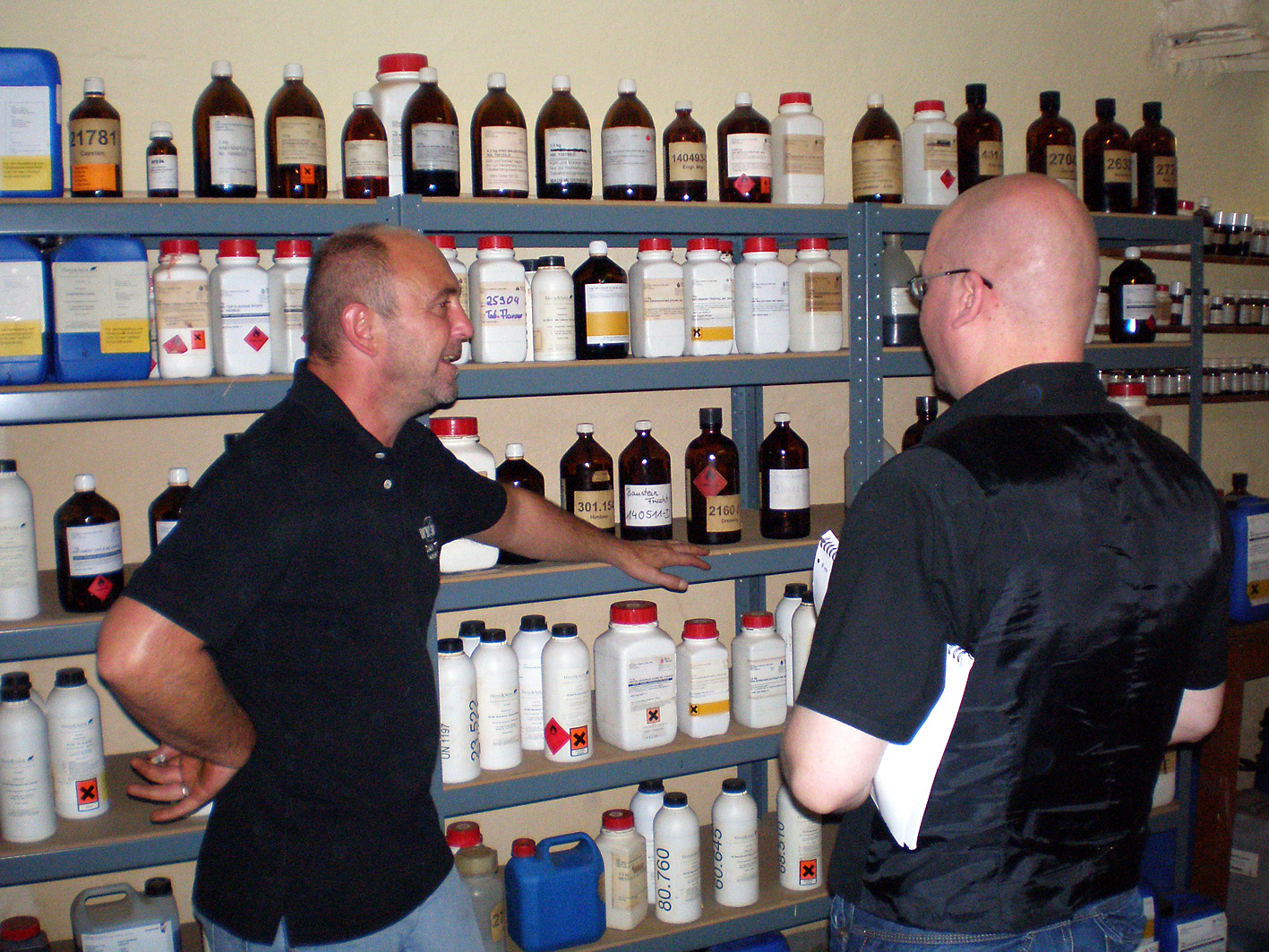
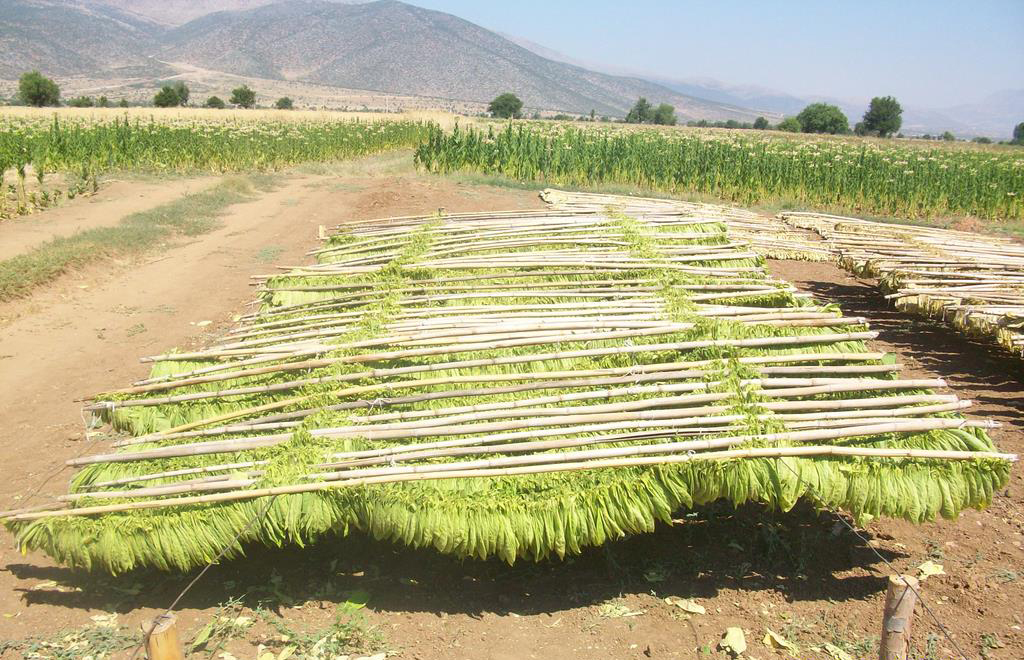
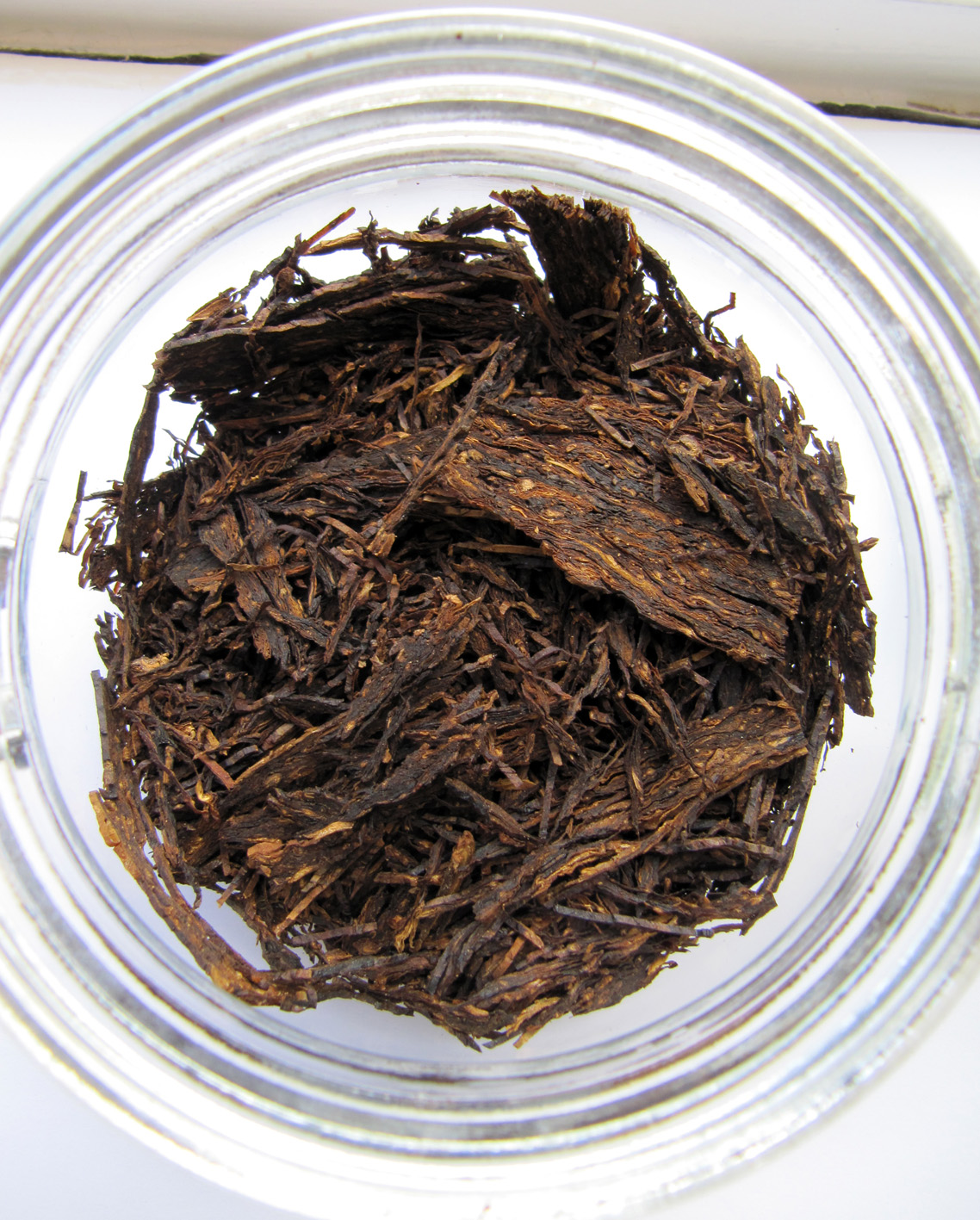
Soon Andreas greeted us. An ordinary looking man on first sight, you could take him for a construction worker if you saw him. Later it turned out that he actually had been a construction worker before he became involved in DTM. In 5 years he learned the tricks of the trade from former master blender Jürgen Westphal, who created almost all original DTM tobaccos and was going into retirement. The tour around the factory started at the top floor where the raw tobaccos are stored in lots of crates, boxes, bales and barrels. I do not know how many tons exactly but with a turnover of approximately 60.000 kg. per year you can imagine the scale of the place. DTM has to buy their leaf tobacco on the same terms as the big companies; by the container. So lots of tobacco have to be stored for quite a while before they are completely processed. Not bad, on the contrary, it can slowly mature and improve its rich aromatic characteristics day by day. The tobaccos come from all over the world. Virginia from Brazil, India, the Philippines and Zambia, oriental tobaccos from Lebanon and Bulgaria, burley from Mozambique and Malawi, latakia from Cyprus, Kentucky from India and perique from the USA.
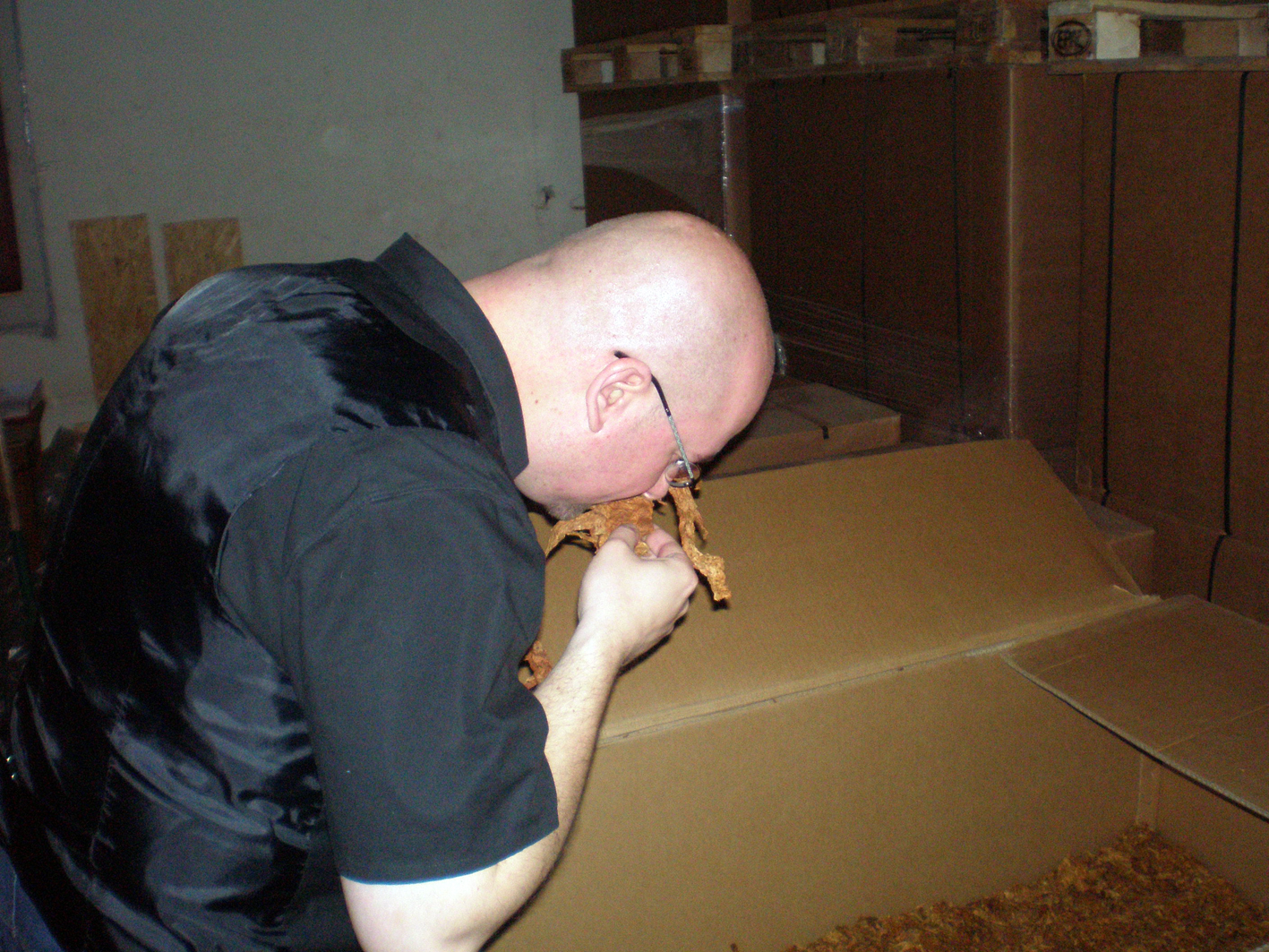
What surprised us was the transparency and openness business-wise in general. “I have so many tons of this and buy it for about that price so and so, etc.” The bottom line is that Andreas is also responsible for the purchase of raw tobaccos. For some of those he must wait nine months after ordering until they are finally delivered (eg. latakia), so he must carefully calculate whether his current stock is sufficient. It was remarkable that the dry, raw unprocessed tobacco indeed had no remarkable smell (long live casings). Well, except latakia and of course perique. Talking about that last one, DTM has a couple of barrels of the stuff, standing in a dark corner. Apparently perique and light are not a good combination. The smell of it is just… Whoaaa….Malevolent..
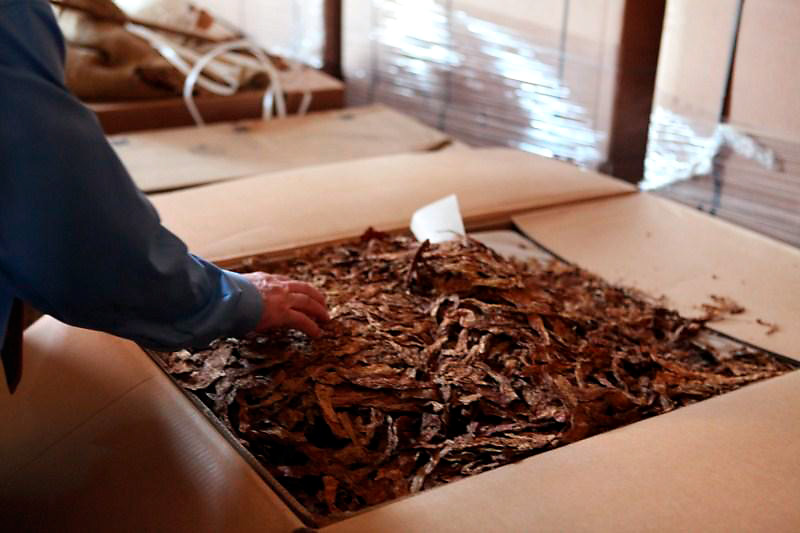 In the next hall upstairs were the ready tobaccos waiting in large boxes to be further processed. Also here nothing was too crazy. Much was made open, it was grabbed, sniffed at. Delicious! I wished I had a couple bags of this tobacco I thought several times. I noticed that most employees smoked shag or cigarettes and no pipe. “Yes, we smoke pure Virginias here and no garbage made by Lucky Strike for example with 70% tobacco and 30% wood chips.” Andreas said. Incidentally he smokes a pipe but with the daily work cigarettes are just easier. Plus he uses cigarettes to try out new raw tobaccos. A trick he learned from Jürgen Westphal. If it does not taste in a cigarette, it certainly does not taste in a pipe.
In the next hall upstairs were the ready tobaccos waiting in large boxes to be further processed. Also here nothing was too crazy. Much was made open, it was grabbed, sniffed at. Delicious! I wished I had a couple bags of this tobacco I thought several times. I noticed that most employees smoked shag or cigarettes and no pipe. “Yes, we smoke pure Virginias here and no garbage made by Lucky Strike for example with 70% tobacco and 30% wood chips.” Andreas said. Incidentally he smokes a pipe but with the daily work cigarettes are just easier. Plus he uses cigarettes to try out new raw tobaccos. A trick he learned from Jürgen Westphal. If it does not taste in a cigarette, it certainly does not taste in a pipe.
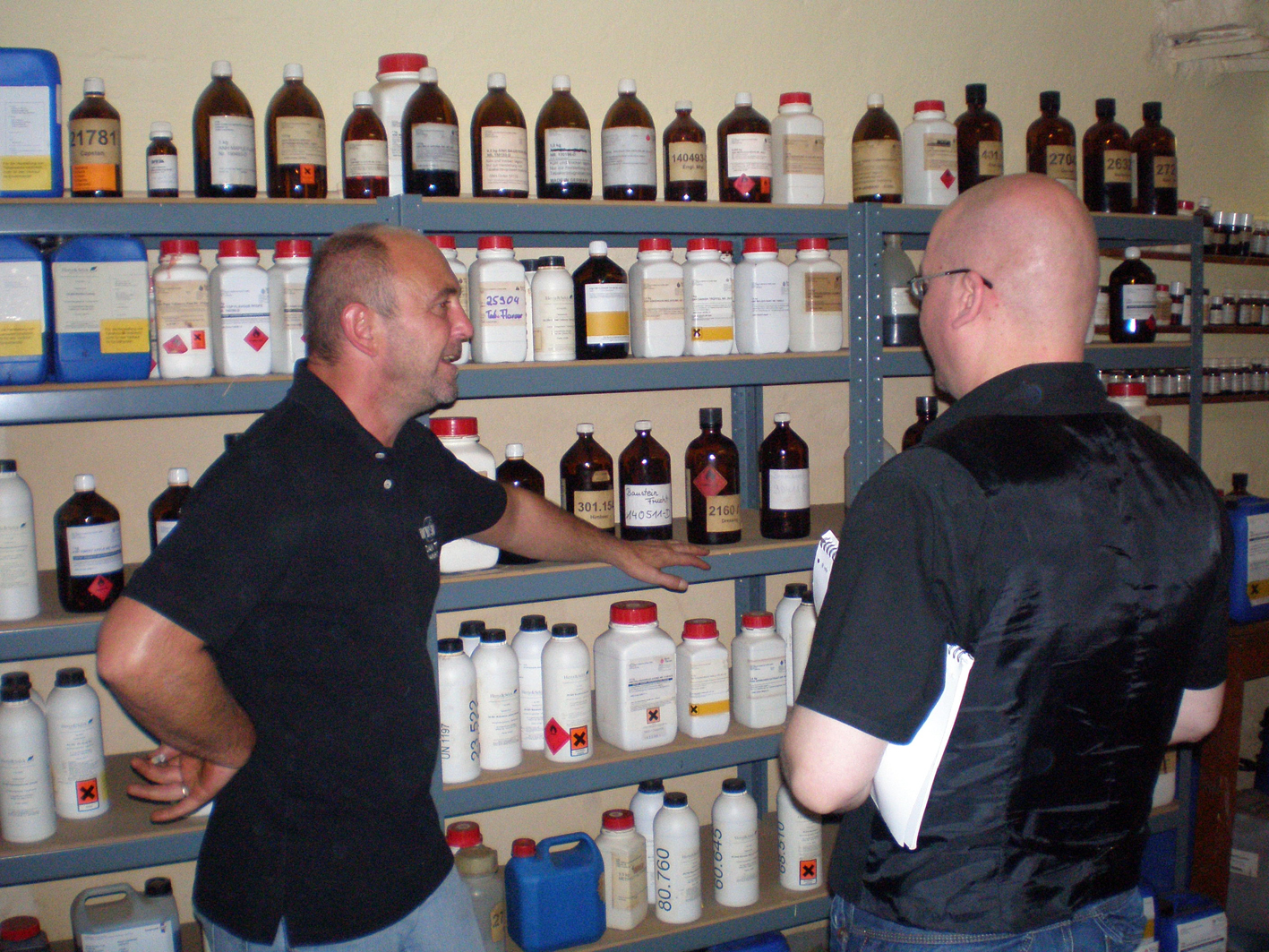
On the lower floor in the building stood the old machinery which until recently was used for the production of tobaccos. Plus there were lots of shelves stacked with all kinds of aromatic extracts. “We are lucky.” Andreas said “The centre for flavour extracts is Hamburg, which is close to Lauenburg. There are many companies which make this stuff so it is very easy for us it acquire.” It was a very strange experience to smell some extracts. Sometimes it smelled so strong, so concentrated, that you could not figure out what exactly was inside a bottle. Also some flavours had several subcategories, for example Butter Vanilla, Crème Vanilla etc.
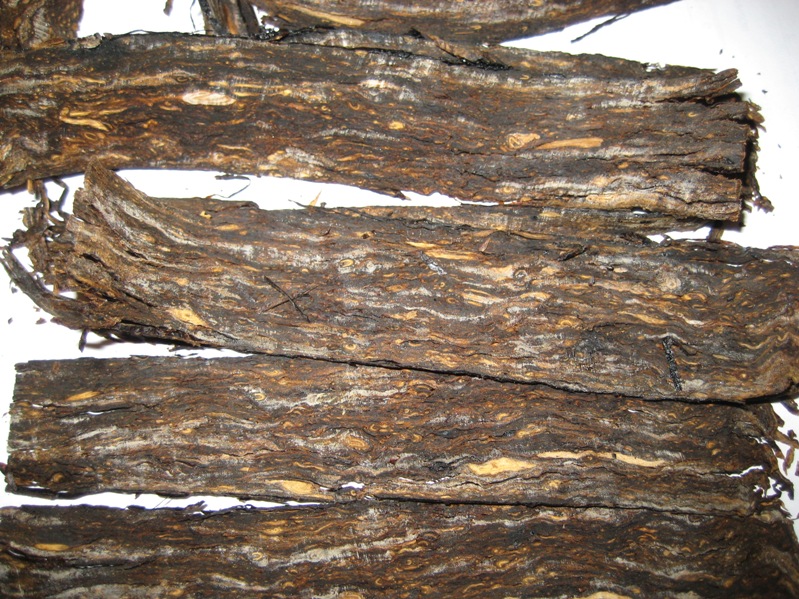
 When we walked around the corner to the next room we saw the mighty flake presses made by famous company Robert Legg from London. Stately red-black devices that looked like they were forged from ancient iron. 2 presses could be heated in order to make Virginia cavendish. However, this was not done because apparently it is cheaper to buy ready-made cavendish. The slabs of flake coming out of the machine are 9 kg. Nice to see that some of those slabs were for Hans Wiedemann’s HU Tobacco, who lets several of his offerings make by DTM. On another wall were so called post–presses. They are needed because the tobacco that comes from the big press has a tendency to expand again. The reason for this is that DTM wants to use Arabic gum (adhesive for the flakes) as little as possible.
When we walked around the corner to the next room we saw the mighty flake presses made by famous company Robert Legg from London. Stately red-black devices that looked like they were forged from ancient iron. 2 presses could be heated in order to make Virginia cavendish. However, this was not done because apparently it is cheaper to buy ready-made cavendish. The slabs of flake coming out of the machine are 9 kg. Nice to see that some of those slabs were for Hans Wiedemann’s HU Tobacco, who lets several of his offerings make by DTM. On another wall were so called post–presses. They are needed because the tobacco that comes from the big press has a tendency to expand again. The reason for this is that DTM wants to use Arabic gum (adhesive for the flakes) as little as possible.
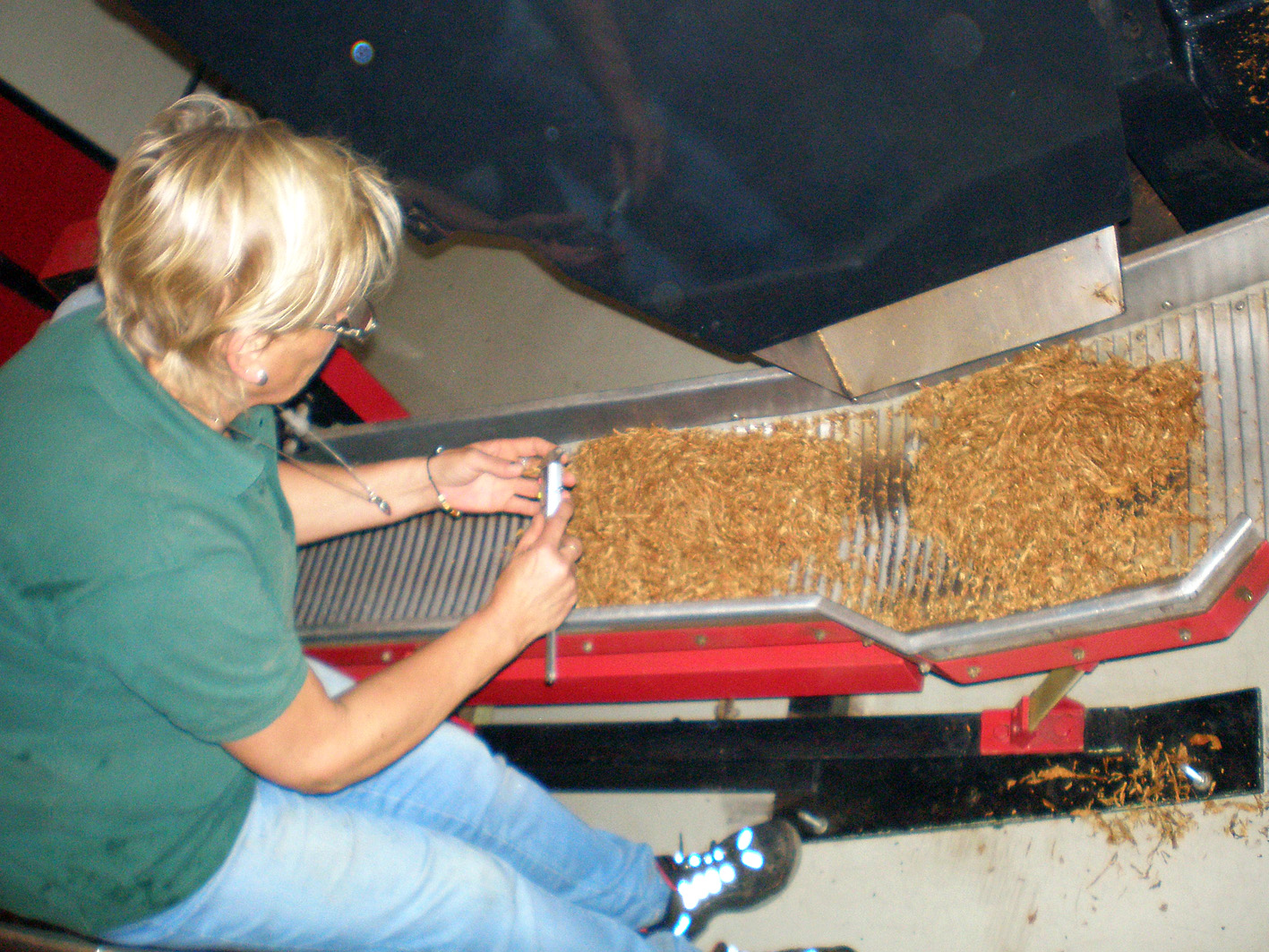
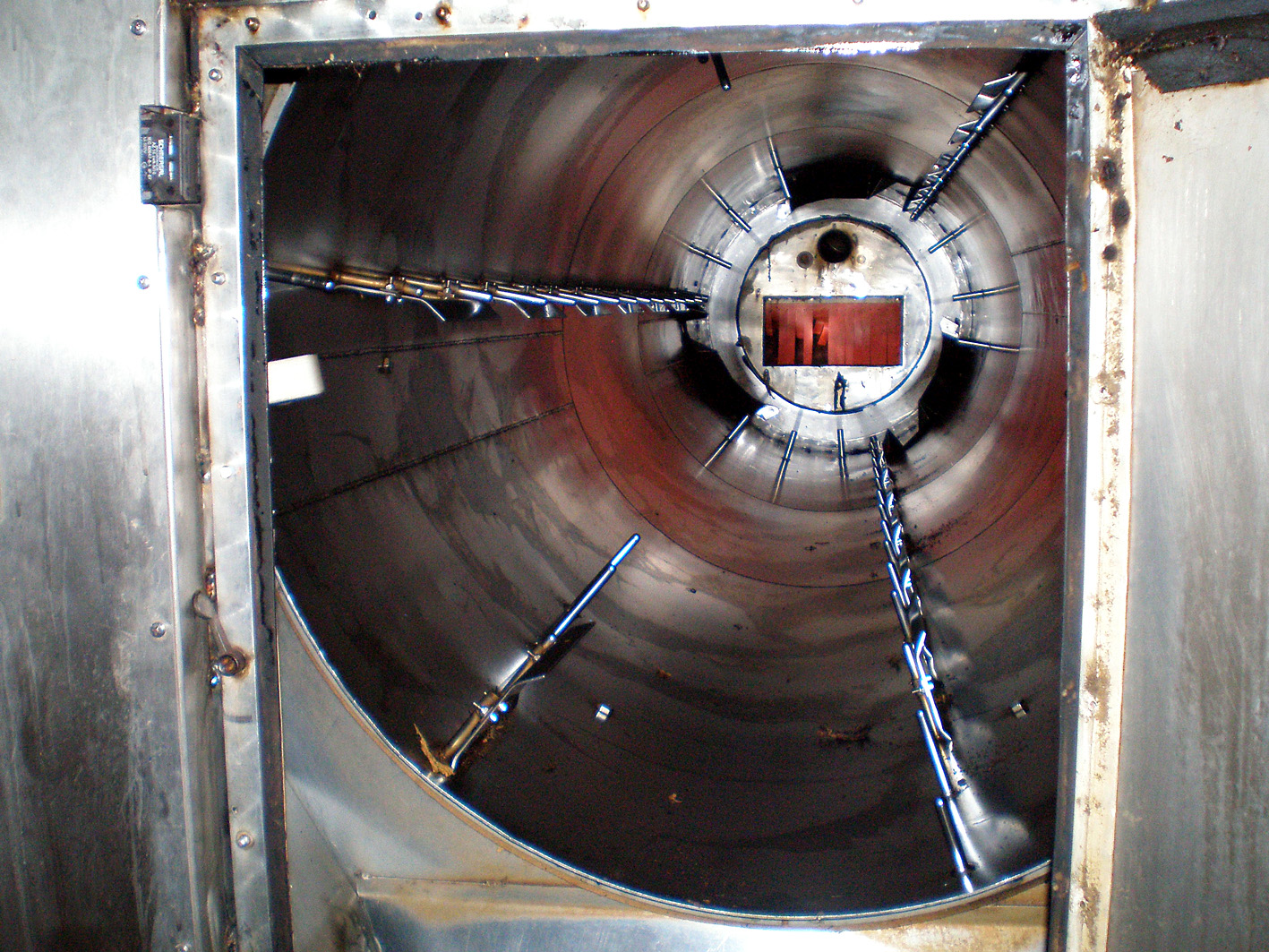
Then we came in the big factory hall, the place of the large, new machine. An impressive sight, especially the big metal cylinder in which the raw tobacco is moistened and cased. Almost everything coming from the DTM factory is cased with honey. Large buckets of the naturally sweet stuff stood beside the machine on the sticky floor. The hall looked slightly blue of the vapours and smoke from the whole process. I will not describe in detail what happens because Ed made a short film about it.
But, in short: The tobacco is moistened/cased, then it gets compressed, cut, the moisture level gets corrected and eventually it all ends up in large boxes. However, the machine which had to cut the tobacco (made by German machine factory Winicker & Lieber who also make the machines for Mac Baren and Pöschl) did not (yet) function optimal. Therefore a little bit of the batch was cut and measured by hand so the machine could be recalibrated. This continued until the cut was right.
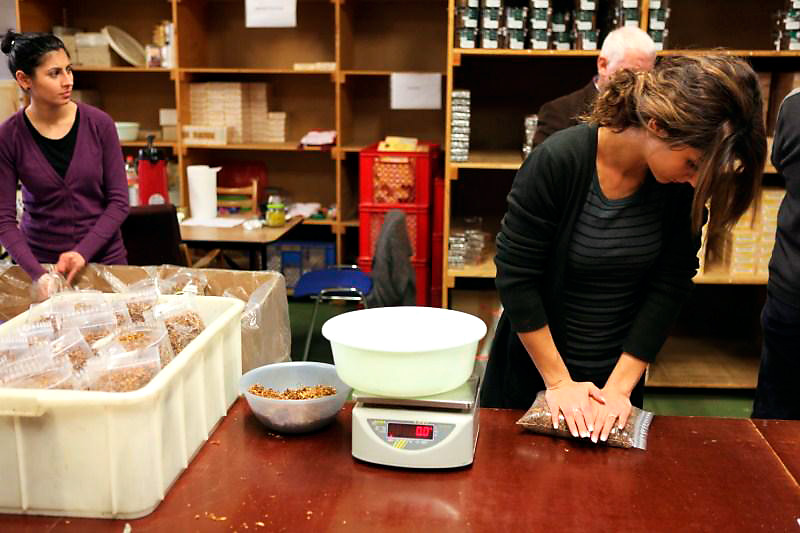
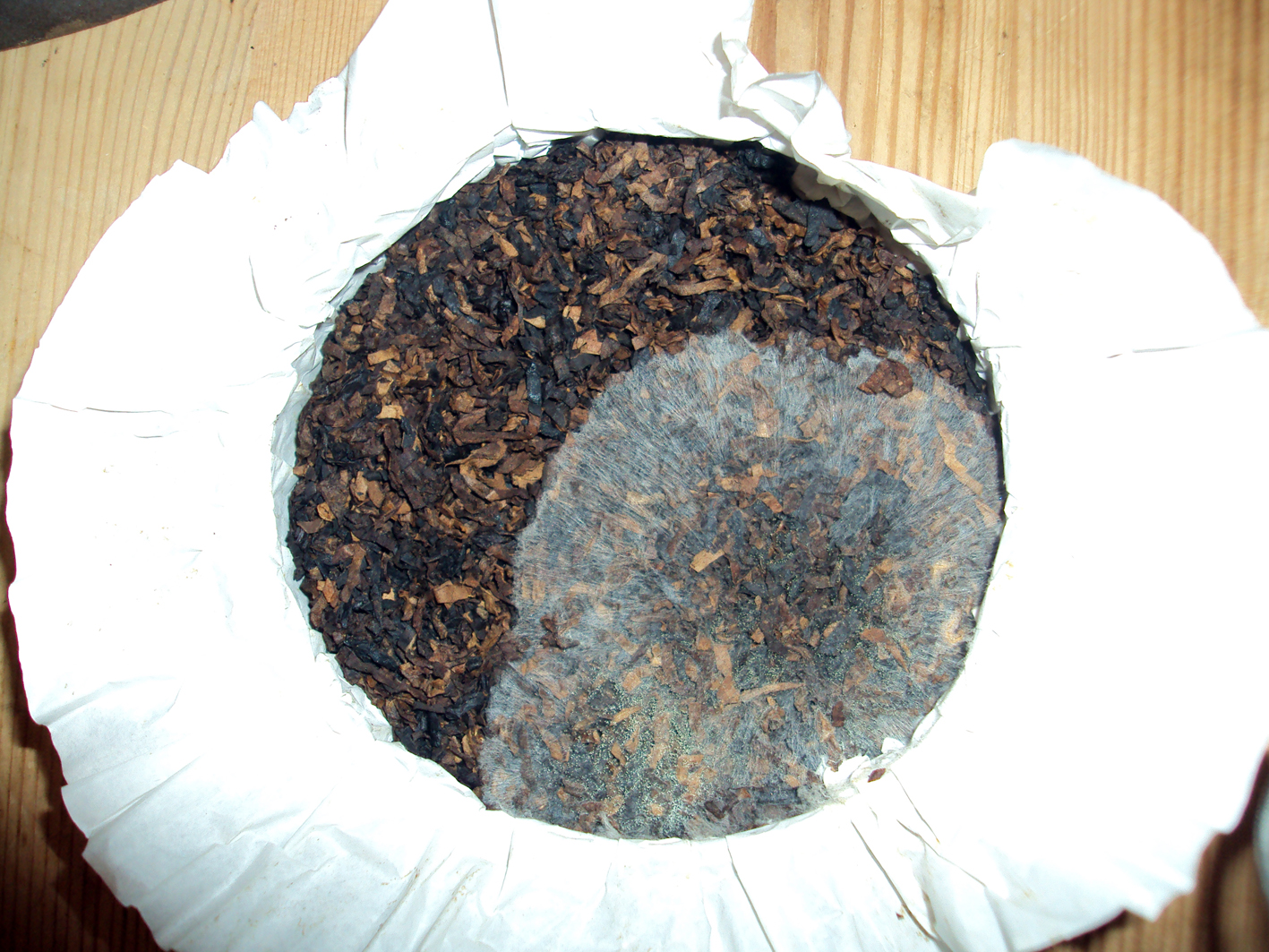
On to the all female packing department. I expected the work was done by machines but nothing could be further from the truth. Everything was done by hand! The tobacco weighing, putting it in tins/pouches, closing the tins/pouches, putting stickers on it.. I have so much respect for the women who do this work. When we were there they were mainly busy with pouches for Switzerland, a very large market for DTM. I had to laugh when Andreas remarked that those pouches contained a blend with 50% oriental tobaccos. “Not good, not good..” He said, and pulled a dirty face. “Up to 30% in a blend, nothing more. But the customer is king.” Also the ladies were packing an aromatic blend of DTM. You could tell right away because the whole room smelled like candies were packed in stead of tobacco. The tour continued in the repair workshop. Pipes are being fixed here by boys who are still quite young. Some pipes shown to me belonged to a man who monthly needed new mouthpieces because he chewed them up. “Pipes are to smoke, not to eat”, Andreas sighed with a smile. From the repair workshop we went to the tobacco warehouse of Dan Pipe. The place where everything in the catalogue (and more) is stored. Impressive to see all those tobaccos and pipe smoking paraphernalia.
Through the tobacco warehouse we came back in the store where Michael Apitz had joined Herr Kaschwich. He is responsible for creating many of the aromatic tobaccos of DTM. And is a walking encyclopaedia of everything that has to do with pipes and tobacco. Plus he is not afraid to share his knowledge and give his opinion, an intense man. I knew little of aromatic tobaccos so it was about time to speak to him. “Herr Apitz, may I ask something…” “No! First I have a question for you! How many tobaccos can one taste and judge on one day?” “Ehrrr, um… Three?” “No! Only one.” And a whole explanation followed. He showed and let us smell a lot of tobaccos together with an explanation of them. Very informative. With one of the first tobaccos which he took from the shelf he asked us what we smelled. As in, you never going to guess it. I smelled it.. And again.. Ehrr, aniseed? He looked at me with big eyes. Correct! *Phewww* Every time we were in the shop and there were no other customers he came up with another topic to talk about. Once again, very informative.
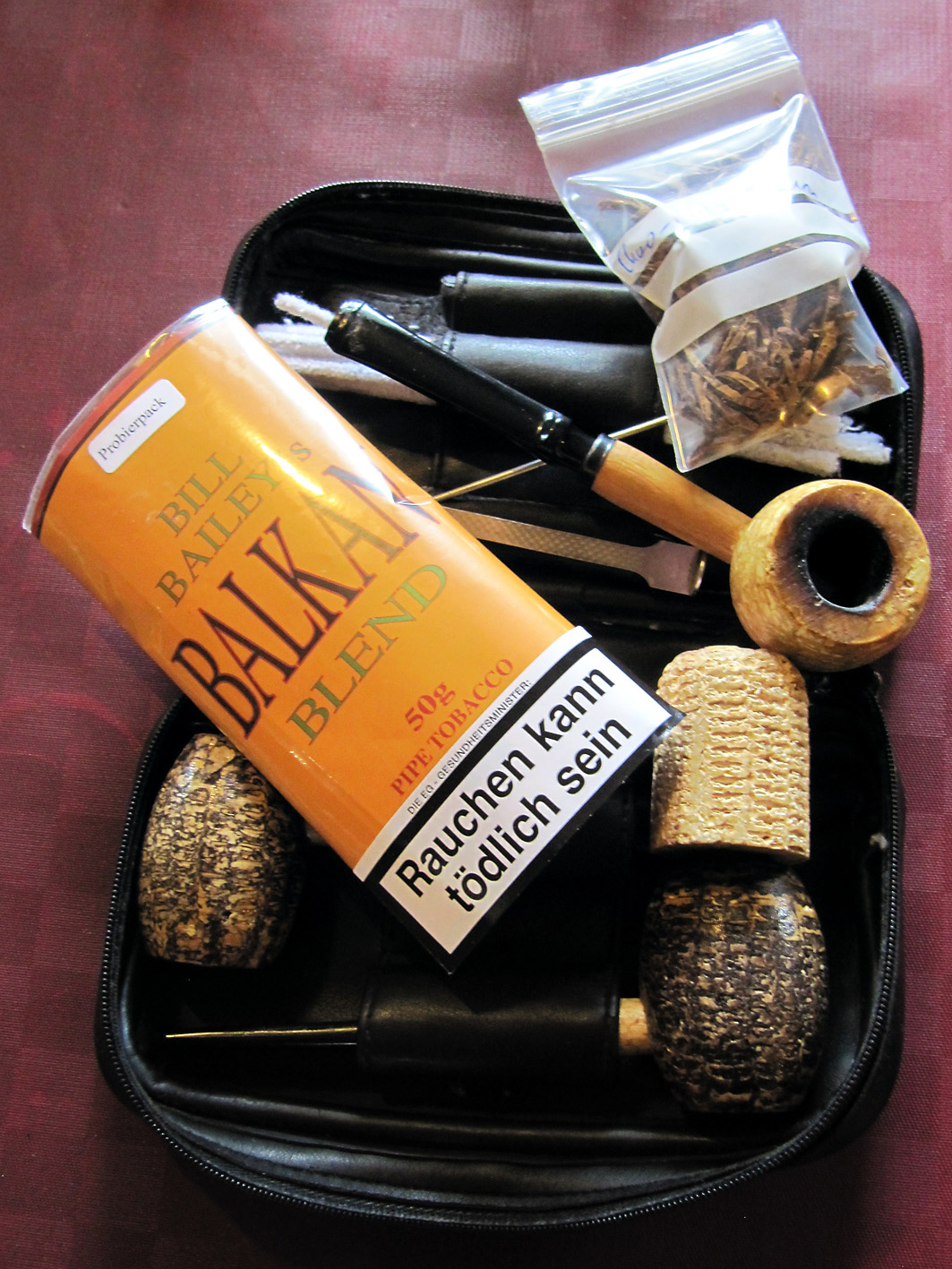 The last time I was there we spoke with each other non-stop for about 1.5 hour until I really had to get back to Ellen, who I left at the Alten Schifferhaus. Just before I went Herr Apitz asked me what I liked to smoke the most. “Well, a good Balkan I guess.” I answered. He then rushed to the tobacco warehouse and came back with a pouch of Bill Bailey’s Balkan Blend. “Here, this is for you, enjoy it!” Which for me characterizes Dan Pipe / DTM. Warm and passionate people with the typical “no-nonsense working hard and effective” German mentality.
The last time I was there we spoke with each other non-stop for about 1.5 hour until I really had to get back to Ellen, who I left at the Alten Schifferhaus. Just before I went Herr Apitz asked me what I liked to smoke the most. “Well, a good Balkan I guess.” I answered. He then rushed to the tobacco warehouse and came back with a pouch of Bill Bailey’s Balkan Blend. “Here, this is for you, enjoy it!” Which for me characterizes Dan Pipe / DTM. Warm and passionate people with the typical “no-nonsense working hard and effective” German mentality.
Here are some DTM-made tobacco recommendations:
– BiBo (Buddies): An ultimate aromatic statement created by Michael Apitz. The absolute pinnacle of sweetness. Forget the sweet American, Danish and Dutch blends, this one tops them all. It tastes and smells like Jaffa cakes, but then into the extreme. I once smoked this one in the evening in my living-room and asked Ellen what she thought. “Well, not bad” was the answer. Until she came downstairs the next morning.. “Whaaaat!? What is this odour? It smells like a friggin’ candy shop in here!” It took a week before we could not smell BiBo any more.. “I rather have you smoking latakia!” Ellen sneered in my direction.
– Bill Bailey’s Balkan: A bit strange, Kentucky in a Balkan, but it works out well and results in a cool and satisfying smoke.
– Midnight Ride: A rich, full flavoured classic English blend. If you want to know how Perique can work its magic in a latakia-mixture, try this one.
– Old Ironsides: A latakia lovers dream. Dark and strong but also cool and creamy this flake makes you come back for more.
– Skipper’s Flake: A no-nonsense straight Virginia flake. Pure unadulterated bright leaf heaven. ‘Nuff said.
– Smooth latakia: One of the newer offerings, created by the wife of Andreas who also works at DTM. Black cavendish combined with latakia make this (like the name says) a smooth smoke. It reminds me a bit of McClelland’s Frog Morton.
– Sweet Vanilla Honeydew: One of the few aromatic tobaccos I really like. Tastes like creamy vanilla and smells like those divine butter biscuits grandma used to bake. A real crowd pleaser.
Thanks go out to Paul and Ed for a lot of the pictures you see.