Tobacco leaf is the main source of flavour and aroma in any tobacco product (Duh!) But aside from latakia and perique (which are stinky enough from themselves) and orientals, raw leaf itself has little smell or taste. And by raw leaf I mean Virginias and burleys, they are almost always cased. For example, I’ve smelled pure and dry Virginias in the tobacco warehouse from the German DTM factory. It made me think of fish-food in stead of the hay-like aroma I am used to. Also tobacco crops vary from year to year, they are not consistent. So flavouring supplements are necessary to create both taste and aroma and help maintain a consistency in them. In the early days tobaccos had a subtle flavouring, but at the end of the 1960’s the high aromatics came into fashion. You know, the kind of blends that dissolve the glazing on your teeth and your girlfriend/wife love. Anyway, additives to tobacco products can be classified in two categories: casings and top dressings (toppings).
Casings: Sometimes you read on labels of tins that a blend for example contains unflavoured Virginia and/or burley. Well, the truth is that very few tobaccos have no flavouring at all. Although a casing can be as simple as sugared water or honey. I know that DTM uses honey for the casing of many of their raw tobacco leaves, the factory floor is pretty sticky because of it. Casings are used at the early stages of tobacco processing to ease the negative qualities of a certain kind of leaf. Ehmm.. Some burleys can be somewhat sour and produce a more alkaline smoke, which can lead to the dreaded tongue bite. The use of a sweetener, a casing containing some sugar, can solve both problems. Some Virginias can be harsh, but also here, with the right casing that can be fixed. In general (of course their are exceptions) casings are not used to flavour the tobacco as much as to make it ready for other processing. Like you make a mild marinade for a piece of chicken to slightly give it a flavour, make it more tender and prepare it for cooking.
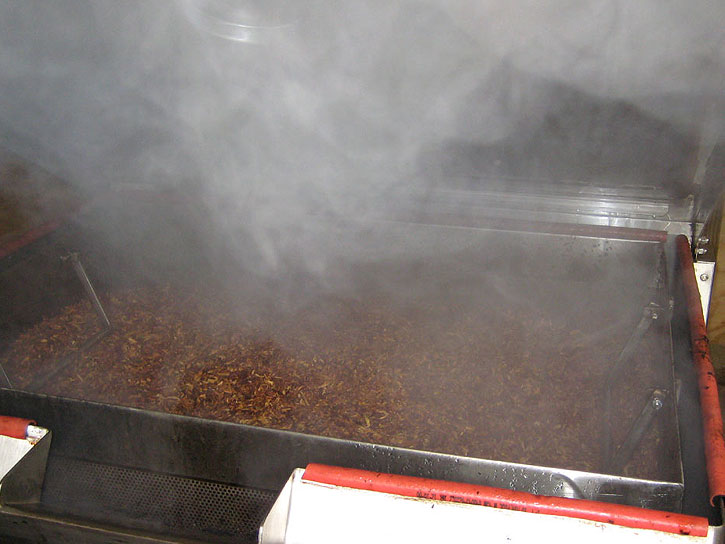
The flavour of a casing should be compatible to the base tobacco that is used. For example, white burley has a certain kind of nuttiness and would match well with chocolate. Which is a commonly used casing for burley. The tobacco which has to cased is put into a machine that somewhat resembles a large clothes dryer with little sprayers on the inside. The casing is then heated and injected into the chamber. Through the use of tumbling, steaming and vacuum pressure the casing works its way into the leaf. Casings are often steamed into the leaf. The steam helps to open the pores and insert the added flavour into the tobacco. Because of this process, casings are usually water-based. After the casing of the tobacco it is dried. Often by putting the leaf on a conveyor which passes through a heated chamber. This reduces the overall moisture content of the tobacco to a level that is more manageable. This level generally is between 12% (pretty dry) and 22% (very moist). The ideal moisture for smoking depends on you, the smoker. But usually it is between 13% and 16%.
The following step will be determined by what the blend is supposed to be. If the intention of the final product is to be an unflavoured blend, for example a Virginia/perique or latakia blend, then the base tobacco is ready to use right after coming out of the heating chamber. The tobacco will be put in a container or something like that in which the finished blend, combined with the other components, is mixed and then is packaged. If the the final product is to be a plug, flake or rope the process starts with raw leaf that will be cased like I told above. After coming out of the casing machine the leaf immediately goes into the press. This because higher moisture is needed to get a good pressing. Or it goes through the drying procedure and is re-hydrated to the right level.
Top dressings (toppings): These are flavourings that most of the time are applied at the end of manufacturing process. That signature flavour, that particular tin aroma, that heavenly room note; all the responsibility of the top dressing. They are usually alcohol-based. When the water based casing is applied, the drying process will bring the tobacco back down to the correct humidity. But at the end of the process the blender wants to avoid having to use heat to re-dry the leaf a second time. So he uses an alcohol-based flavouring and allows the tobacco to rest for a couple of days. The alcohol will evaporate which leaves the concentrated flavour behind with little additional moisture.
Most casings and top dressings contain a “fixing agent” to assure that the flavourings will stick to the leaf and remain stable until used. In addition to fixing agents hygroscopic agents are used. Hygroscopic agents are chemicals used to control the moisture content of tobacco. They prevent the tobacco from becoming too dry in a dry climate or from picking up moisture in a humid area. The most widely used agents are sorbitol, propylene glycol and glycerine.
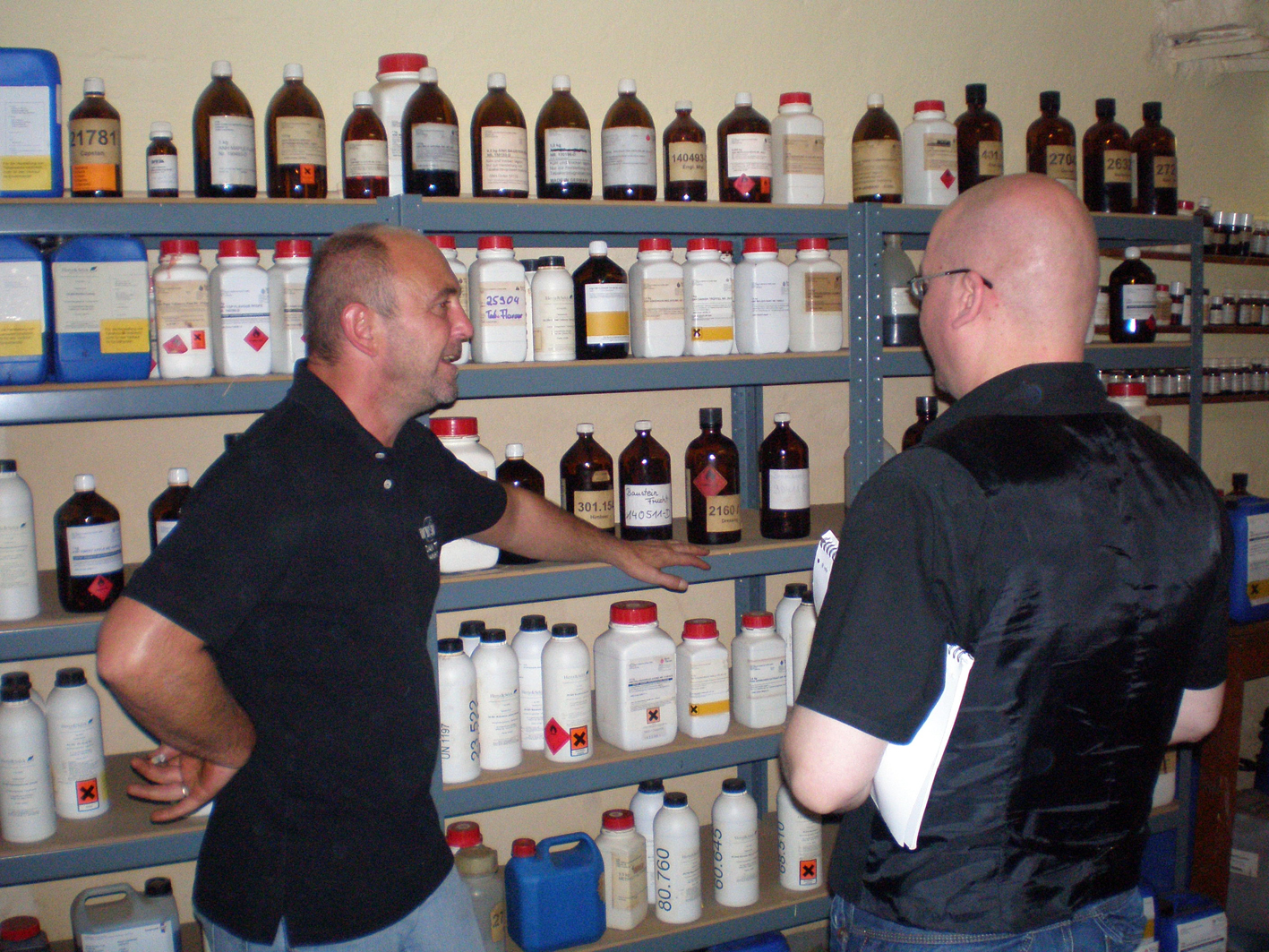
Concentrated flavourings are preferred by most tobacco blenders. This because the extract/concentrate can be manufactured much more uniformly and is less subject to changes while being stored than natural flavourings. When I visited the DTM factory I saw shelves and shelves full with all kinds of concentrated flavourings. According to master-blender Andreas Mund the city of Hamburg (pretty nearby the factory) is the centre of the world for concentrated flavourings. Lucky DTM! It was a strange experience when I opened up some of the flasks and bottles and sniffed the contents. You read something on the label like “chocolate” and when you smell it you absolutely don’t recognize it because it is THAT concentrated. So it won’t be a surprise that some blends use as little as 8 tablespoons of fluid per 100 pounds of tobacco.
Here are some of the most common flavourings:
– Chocolate is manufactured as a natural product from the coco bean. It may be fortified with some cocoa which is synthetically produced.
– Fruit flavours are obtainable in both natural and synthetic form. Natural fruit flavours are extracted from processed fruit.
– Licorice comes from the licorice root and can be fortified with synthetic chemicals.
– Menthol can also be made synthetically or it can be used in its natural state which is distilled from peppermint oil.
– Rum used in tobacco is most of the time the Jamaican type. Jaaah man! It can also be synthesized.
– Vanilla can be used in its natural form but for the most it is manufactured synthetically.
– Wine flavours are as varied as the types of wine available: burgundy, sherry, madeira, etc.
It is very difficult to create a good aromatic blend. You have to take in consideration the natural aroma of the leaf plus whatever the casing adds. Virginias often have a hay-like aroma and if that is not taken into account you could end up with something entirely different than you were hoping for. Also certain flavourings take advantage of other ones. A bit of vanilla boosts the taste of chocolate. Or flavourings have a tendency to overpower others, like coconut. And then there are flavourings that just don’t match with tobacco in general. For example, Paul has always looked for a blend with a nice banana-flavour and has not found one yet. Banana and tobacco.. Should work one would think. Well, I spoke with aromatic master-blender Michael Apitz from DTM and asked him why they did not have any blends with banana-flavour. He took me to the warehouse and showed some old tins with… Banana flavoured blends. “You know, there is a reason we don’t sell them any more and why they are collecting dust in the warehouse” he said. “They just don’t taste good and because of that people won’t buy them.” So it may take a whole lot of trying out before the aroma of a blend is acceptable.
And if you want to know why most aromatics don’t taste like they smell, have a look here: Who’s afraid of chemistry? (by Paul)
 These days every blender anywhere on the globe can make a high aromatic. But back in the days in the United Kingdom they had the “Tobacco Purity Law”. This law prohibited blenders from the use of large amounts of artificial flavourings and hygroscopic agents in the manufacture of tobacco products. In the early years of the Dunhill store Alfred Dunhill himself used to experiment at home with the creation of new blends. Regularly he got visits from police-officers who thought they smelled illegal things going on.. There was a list of additives that were approved and which had to be dissolved in alcohol or water. BUT they could only be applied at small percentages. For example, it was estimated that less than 0,5% of the weight of any given brand, manufactured in the United Kingdom, consisted of flavourings. This stood in contrast with some brands manufactured in the United States. There sauces constituted as much as 25% of the gross weight of the tobacco product. And in the case of Dutch tobaccos, this number was as high as 35%. So the blenders in the United Kingdom had to use the best quality tobaccos available, primarily the Virginia-type ones, orientals and condiment leaves like latakia and perique. And of course they had to have to skills to create outstanding mixtures. This with the help of all kinds of processing techniques such as stoving, toasting, panning, steaming and pressing. It wasn’t until the 1980’s that the Tobacco Purity Law was abolished by the Thatcher government so that American tobaccos could be sold in the United Kingdom.
These days every blender anywhere on the globe can make a high aromatic. But back in the days in the United Kingdom they had the “Tobacco Purity Law”. This law prohibited blenders from the use of large amounts of artificial flavourings and hygroscopic agents in the manufacture of tobacco products. In the early years of the Dunhill store Alfred Dunhill himself used to experiment at home with the creation of new blends. Regularly he got visits from police-officers who thought they smelled illegal things going on.. There was a list of additives that were approved and which had to be dissolved in alcohol or water. BUT they could only be applied at small percentages. For example, it was estimated that less than 0,5% of the weight of any given brand, manufactured in the United Kingdom, consisted of flavourings. This stood in contrast with some brands manufactured in the United States. There sauces constituted as much as 25% of the gross weight of the tobacco product. And in the case of Dutch tobaccos, this number was as high as 35%. So the blenders in the United Kingdom had to use the best quality tobaccos available, primarily the Virginia-type ones, orientals and condiment leaves like latakia and perique. And of course they had to have to skills to create outstanding mixtures. This with the help of all kinds of processing techniques such as stoving, toasting, panning, steaming and pressing. It wasn’t until the 1980’s that the Tobacco Purity Law was abolished by the Thatcher government so that American tobaccos could be sold in the United Kingdom.
Recommended aromatic blends are:
– Cornell & Diehl: Autumn Evening
– DTM: BiBo, Blue Note, Mediterraneo, Memories of Tuscany, Sweet Vanilla Honeydew
– HU Tobacco: Geniet Moment
– Lane Ltd.: 1-Q, Captain Black White
– Mac Baren: 7 Seas Regular Blend*
– Neptune*
– Peterson: Sunset Breeze*
– Planta: Danish Black Vanilla*
– Stanwell: Melange*
– Sillem’s: Black
– Winslow: No. 1*, Harlekin*
– WO Larsen: Fine & Elegant*
* Available in The Netherlands