Perique is the pepper of the tobacco world. It spices up and enhances all kinds of mixtures when used moderately. But use it too much and it destroys a blend.
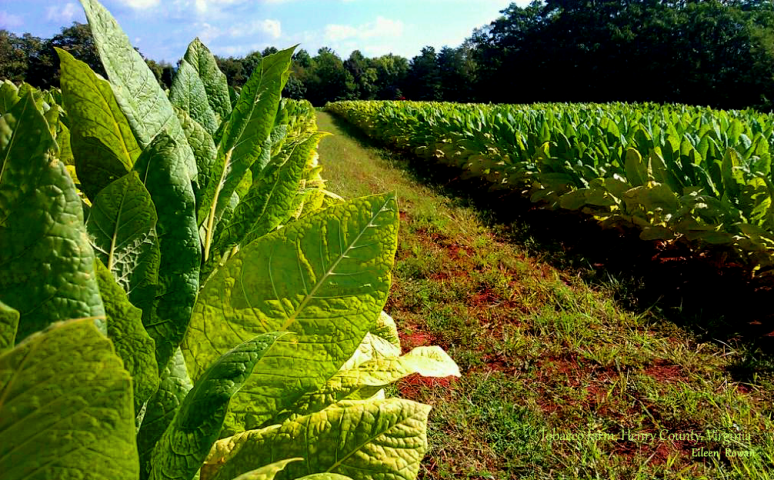
Around 1776, French-speaking settlers from Canada (the Acadians) moved into the area of Saint James Parish, Louisiana. They saw that the Choctaw and Chickasaw tribes were cultivating a variety of tobacco with a distinctive, spicy, fruity flavour. These native Americans had a special way of preparing it. They would pack leaves tightly into a hollow log and put a heavy rock on it. Pretty similar to how it is done today, but later more about that.
A farmer named Pierre Chenet was the first to begin raising the local tobacco commercially in 1824. Chenet’s nickname was “Perique,” hence the name. He is also credited with refining the fermenting process (which gives perique its unique flavour) through the technique of pressure-fermentation.
This process of producing perique remains a traditional craft. Not much has changed since the early 20th century.
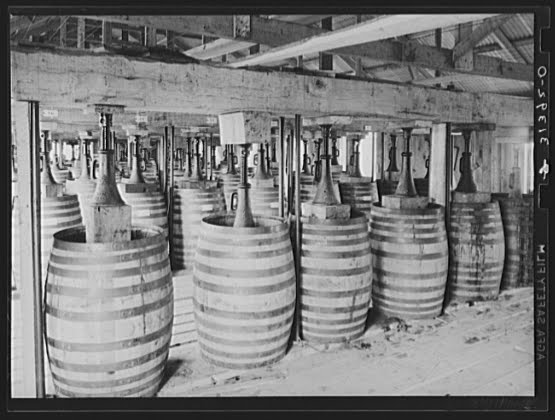
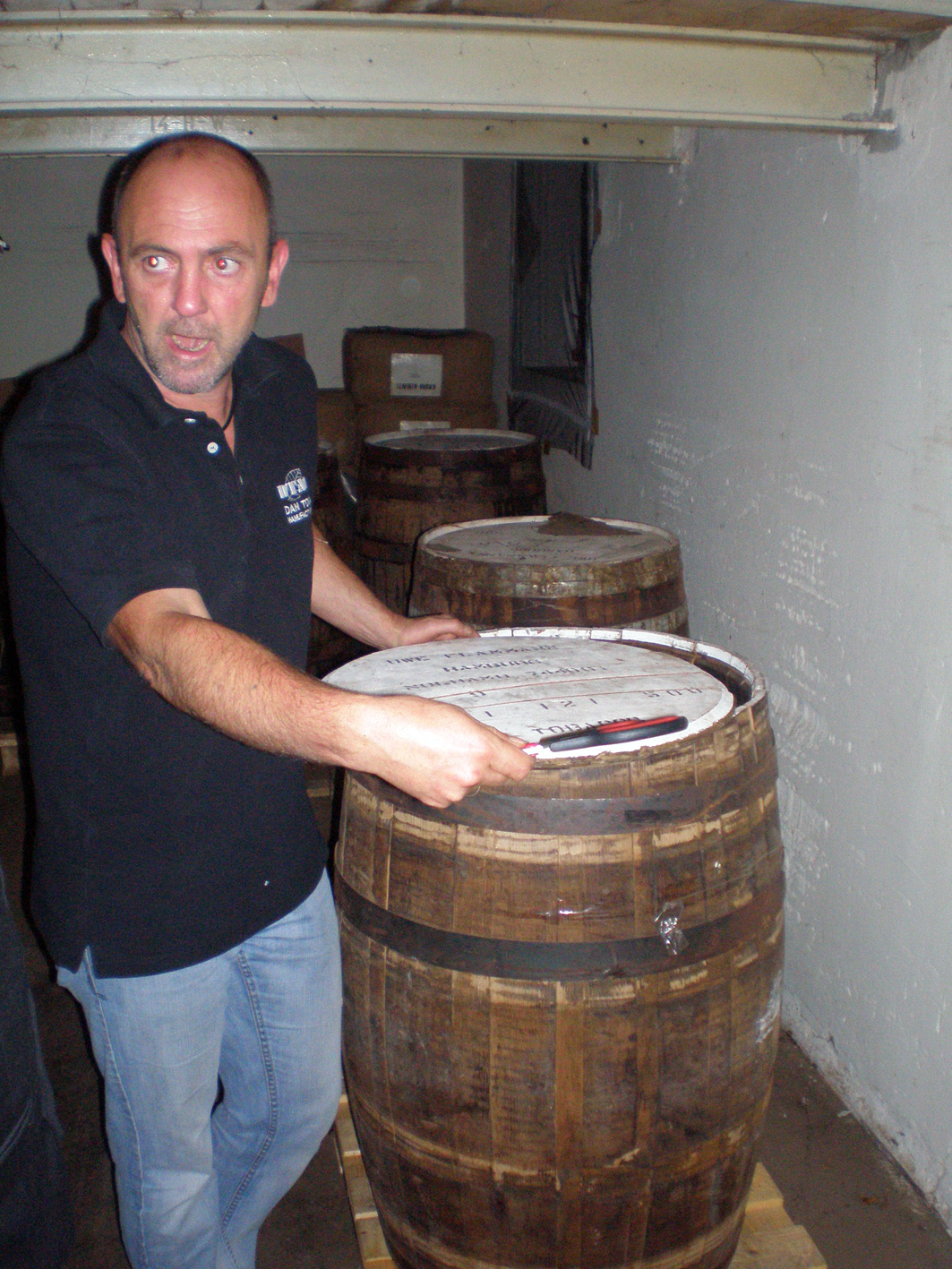
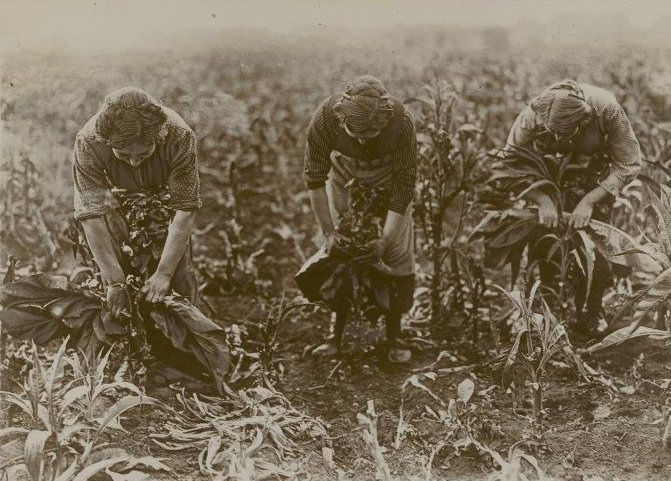
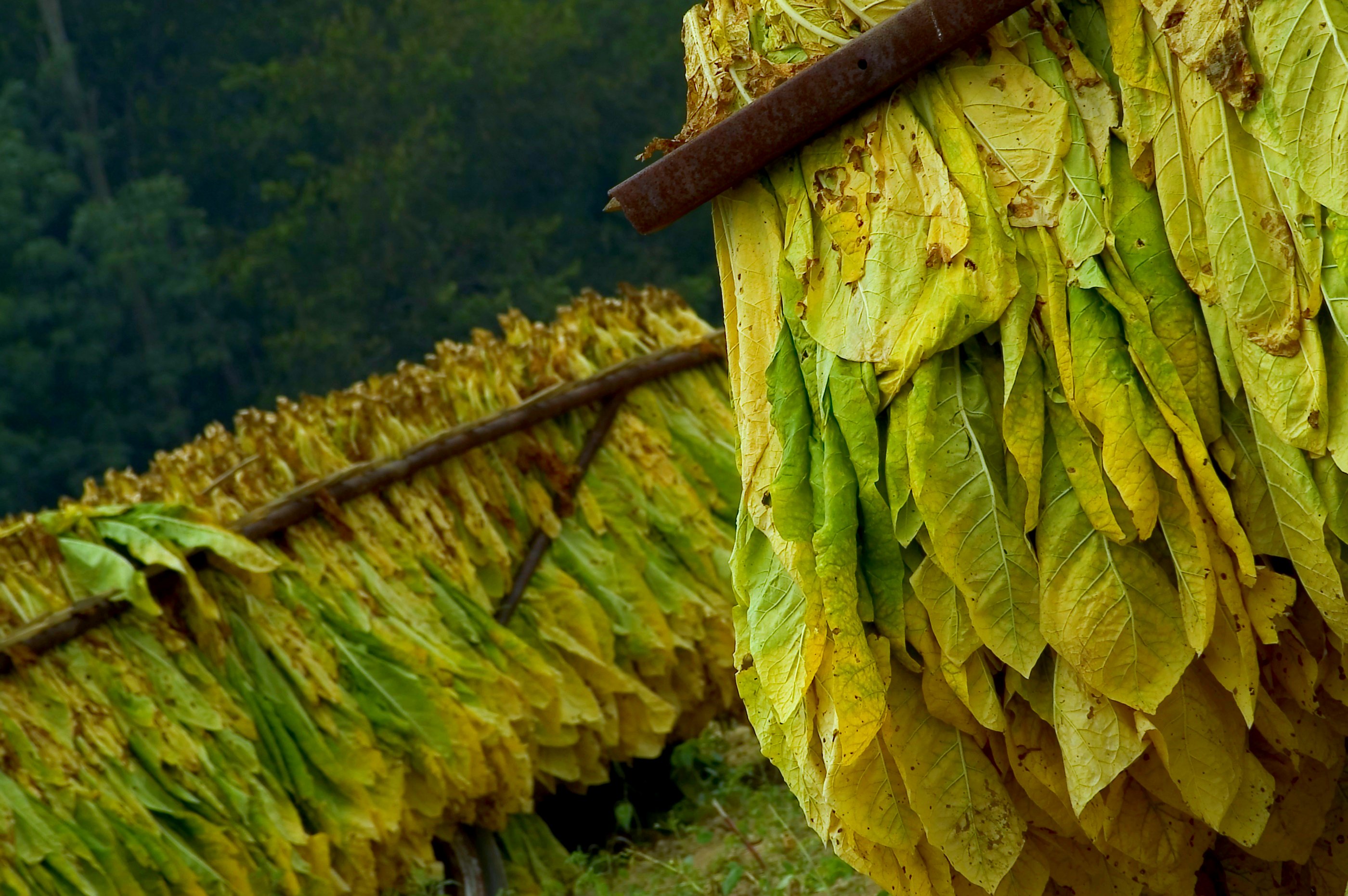
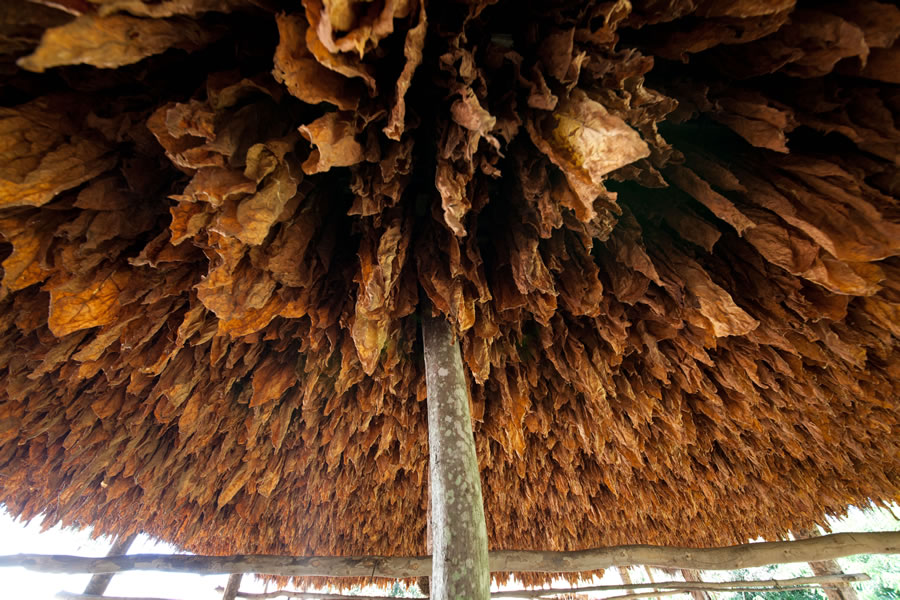
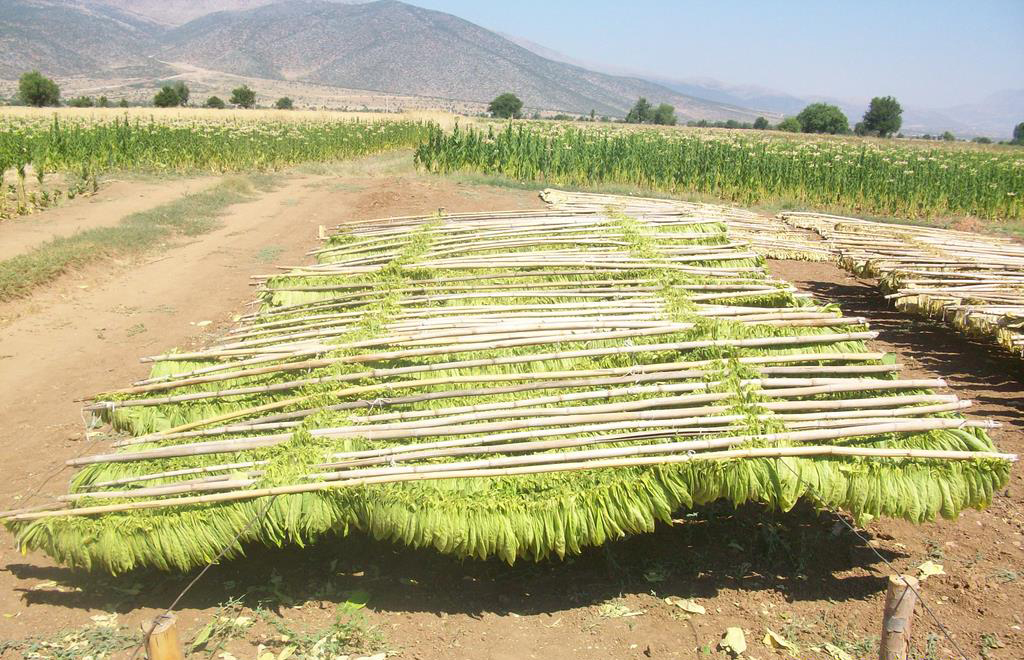
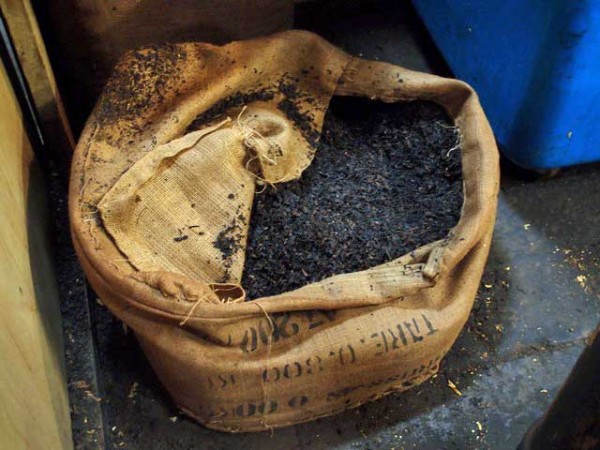
First air cured tobacco is hand stripped. The leaf which is used is considered to be pretty similar to burley. The only moisture added is just prior to the stripping to make the leaves pliable. How many moisture is used is up to the craftsmen. You just have to feel it. Then the tobacco is rolled into “torquettes” of approximately 1 pound (450 g) and packed into hickory whisky barrels. These are topped off with a wooden lid and pressed by using oak blocks and massive screw jacks. Thus forcing nearly all the air out of the still moist leaves. The barrels are unpacked at least three times during the active fermentation phase (around five months). The torquettes are then repacked in the barrels in reverse order (former top bundles on bottom and bottom bundles on top) to permit a little air back into the tobacco. They are then closely monitored with periodic increases of pressure.
After at least a year of this treatment, the perique is ready for consumption. But the longer the barrels are sealed and pressure is applied, the more complex the flavour notes become. The finished tobacco is dark brown (nearly black) and very moist with a fruity, slightly vinegary aroma that carries a hint of alcohol. The fruity aroma and hint of alcohol are the result of hundreds of volatile compounds created by anaerobic fermentation of the tobacco. Many of these are responsible for the flavours of fruits and are often found in wine. Talking about alcohol, there even is a perique liqueur!
There are 2 different types of perique. St. James perique is made by using the method above. The other one is called Acadian perique. It is made by processing Green River burley in the same manner as the St. James version. The two types are almost always blended together for use in various mixtures. But to be able to use the name “perique” it has to contain some St. James. Of course some people tried to grow perique outside Louisiana, then use a similar processing method and mix it with the real stuff.. Awful.. Fortunately, no legitimate companies are using this kind of tobacco. No, real perique only grows within the St. James Parish area. Some scientists believe that it sits on top of a mineral deposit that gives the tobacco its robust and distinct flavour.
At one point in the recent past, the future of Perique did not look well. Farmer Percy Martin had been producing the tobacco for years. But when the numbers of pipe smokers declined, the usage of perique declined. Struggling to find a new market, Percy began mailing samples to potential buyers. That is how Santa Fe Natural Tobacco caught wind of his rare brand of tobacco. So the lion’s share of Percy’s output went to that company for the usage of American Spirit cigarettes and rolling tobacco in 2000. But at least he did survive and after his death in 2012 his son Ray took over the business.
Fortunately the production of perique seems to be secured now. Pierre Chenet’s granddaughter, Coralie Decareau, married Celestin Poche in February, 1829. And the Poche family has been involved in the cultivation and processing of perique through current times until Mark Ryan bought the firm in 2005. Ryan has doubled production since that time ans soon the production capacity will even quadruple to 400 barrels annually. Ryan is able to ensure supply because he has increased prices to the farmers and eliminated their labour of stripping the leaves. As a result, St. James Parish farmers are once again interested in growing tobacco.
Perique is a very versatile tobacco. When you use it with deep, heavy tobaccos like matured Virginias and/or dark burleys it adds a mellow sweetness that tends to reduce the sharpness of those. When used in a more mellow blend it can add a bit of tang and spice. And if you have got a blend that lacks richness and depth a bit of perique can resolve that problem. It also can help slow down the burn rate of a blend. That is why it is so often used in Virginia blends which tend to burn fast and hot. What you then get is a so called VaPer.
Being a condimental tobacco, perique is usually used sparsely in a mixture. Also because it has a fairly decent amount of nicotine. Beware, over time perique will mellow out in a blend.
– 1% to 2%: enhances flavour without making its presence known
– 2% to 4%: the presence can be detected. Its absence would be noted because the flavour of the blend would be subdued. Like listening to music with ear-plugs.
– 4% to 8%: perique really begins to make itself known. Like a voice that you softly hear.
– 8% to 12%: yes, there definitely is perique in this blend! You can notice it very well.
– 12% to 20%: a good working maximum. Unless your name is Aleister Crowley. He smoked straight perique soaked with rum. The Beast…
Recommended blends with perique are:
– Ashton: Artisan’s Blend*
– Cornell & Diehl: Kajun Cake, Bayou Morning, Old Joe Krantz
– DTM: St. Bernard Flake, Midnight Ride
– Dunhill: Deluxe Navy Rolls, Nightcap*
– Escudo Navy Deluxe
– Esoterica: Dorchester, Dunbar
– GL Pease: Fillmore, Haddo’s Delight, Telegraph Hill, Chelsea Morning, Triple Play
– Hearth & Home: Anniversary Kake
– HU Tobacco: Janneman Flake, Louisiana Broken, Edward G, Director’s Cut
– J. F. Germain & Son: Royal Jersey Perique
– MacBaren: HH Acadian Perique
– McClelland: Bulk No.2015 Virginia Flake, Personal Reserve: St. James Woods, PCCA Tudor Castle, PCCA Beacon
– Orlik Golden Sliced*
– Peter Stokkebye: Luxury Bullseye Flake, Luxury Navy Flake
– Samuel Gawith: St. James Flake
– Solani: 633 Virginia Flake with Perique*
– Wessex: Brigade Sovereign Curly Cut
* Available in The Netherlands



























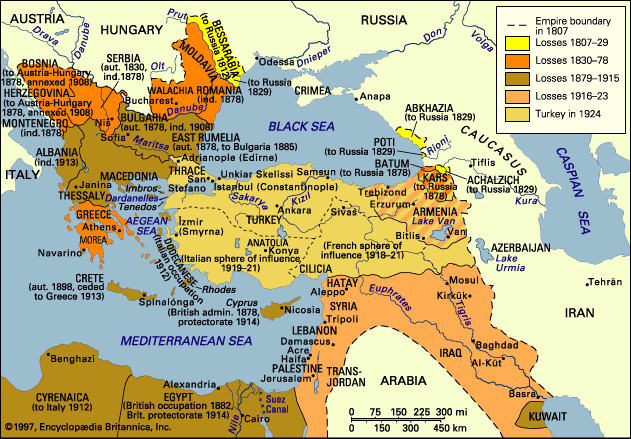
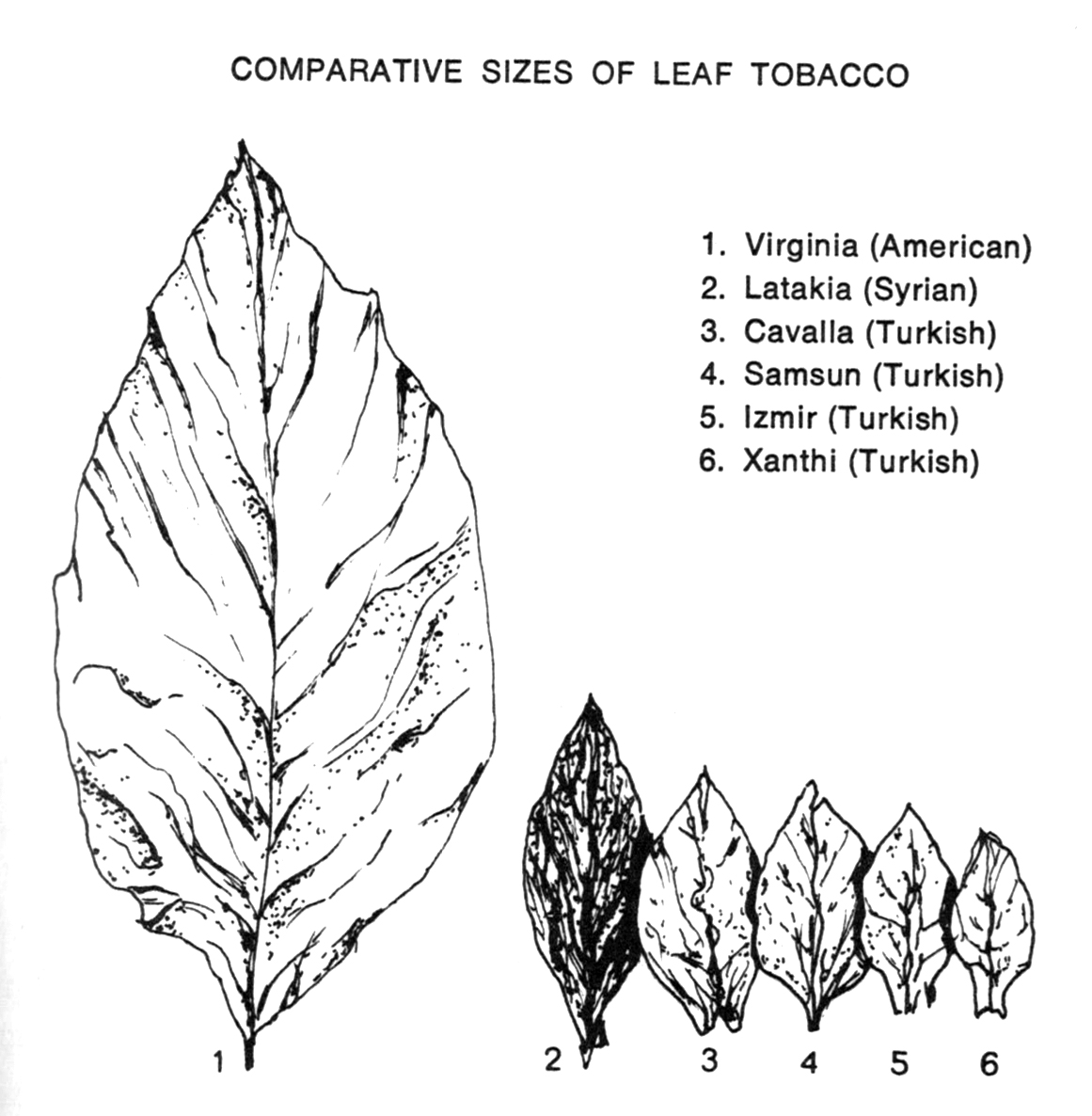




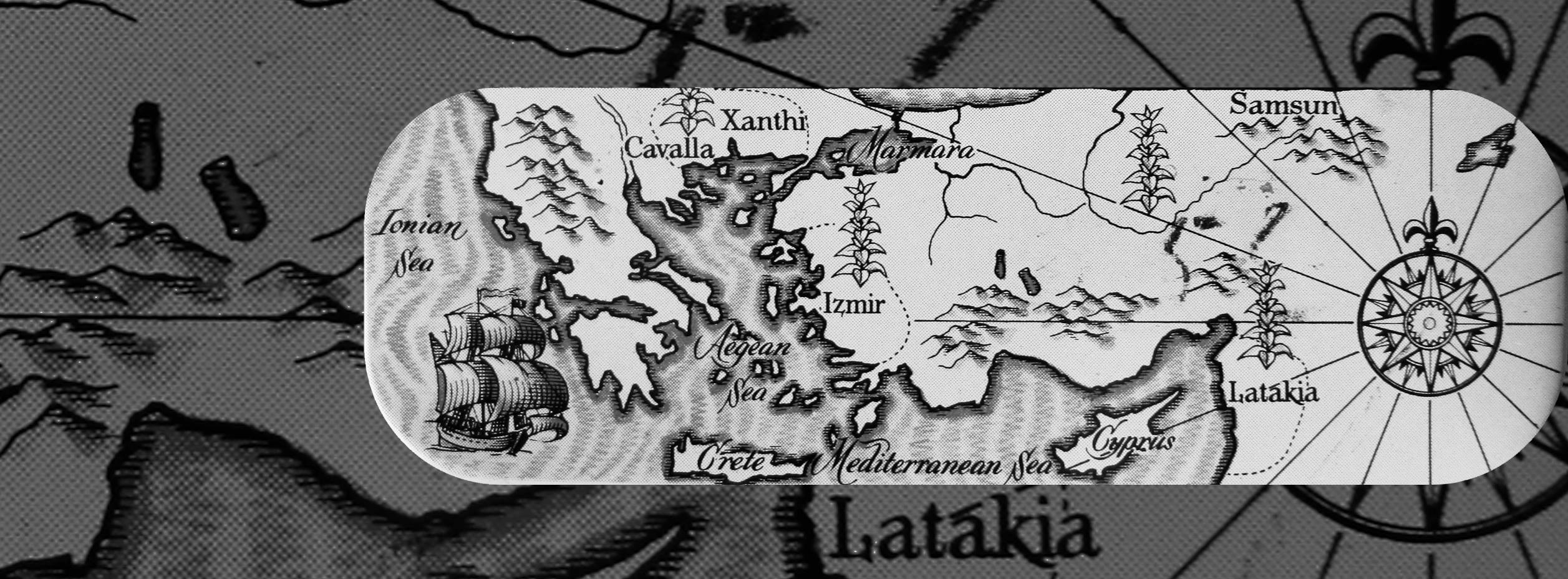 Somewhere during the 80’s the Syrian government lifted the moratorium and to some extent the production was resumed. But it never came close to the amounts of the pre-1960 era. The demand was lower because there were less pipe smokers. On top of that Syrian latakia had to compete with the dark leaf that came from Cyprus. Also a lot of the experienced processors had found another job. As a result the quality of latakia made by other makers became shaky, inconsistent.
Somewhere during the 80’s the Syrian government lifted the moratorium and to some extent the production was resumed. But it never came close to the amounts of the pre-1960 era. The demand was lower because there were less pipe smokers. On top of that Syrian latakia had to compete with the dark leaf that came from Cyprus. Also a lot of the experienced processors had found another job. As a result the quality of latakia made by other makers became shaky, inconsistent.

