One of the highlights of the year for me is always a visit to the Lohmarer Pfeifenmesse (Lohmar pipe-show) the first Saturday in May. So you can imagine the shock when I first heard that this years pipe-show would be the last one. What?? No more Lohmars? Disbelieve.. You know, beyond all the exhibitors with their beautiful wares I mostly enjoyed the atmosphere created by all the pipe-smokers. I met so many lovely people there. Organizer Volker Bier explained it all in a YouTube video. For those of you who don’t speak German, in a nutshell it comes to this: Next year the location where the pipe-show is always held, Villa Friedlinde, is getting a big renovation. So no activities then. Also Volker had enough of organizing the show year in year out. All those years were great, but now it is enough. Luckily two friends of Volker, Kelvin and Toto, stepped in. I was immensely happy to hear that next year a brand new pipe-show is organized by them in Hamm on May 16th.
Back to this year. Normally I would have drove along with good friend Rob, except he could not make it, he had to work. Regarding pipe-meetings it is “the more the merrier” so I asked Mark (the organizer of the annual Dutch pipe smokers forum Zutphen meeting) if he wanted to tag along. He was happy to go together with me. Only, one day before the pipe-show he texted me and I had to silently laugh a bit. The week before Lohmar Mark started in the gym, his first time ever. Being enthusiastic in trying to shed some weight, gain some muscle and improve his condition he tirelessly outdid himself. Only to discover that the next morning he could not get out of bed because of all the muscle pain. “If this continues I won’t be able to go with you tomorrow.. I can’t even get in the car this way!” he said. “Just relax and let me know early in the morning.” I answered. I was happy that apparently the aches lessened because Mark felt good enough to visit Lohmar.
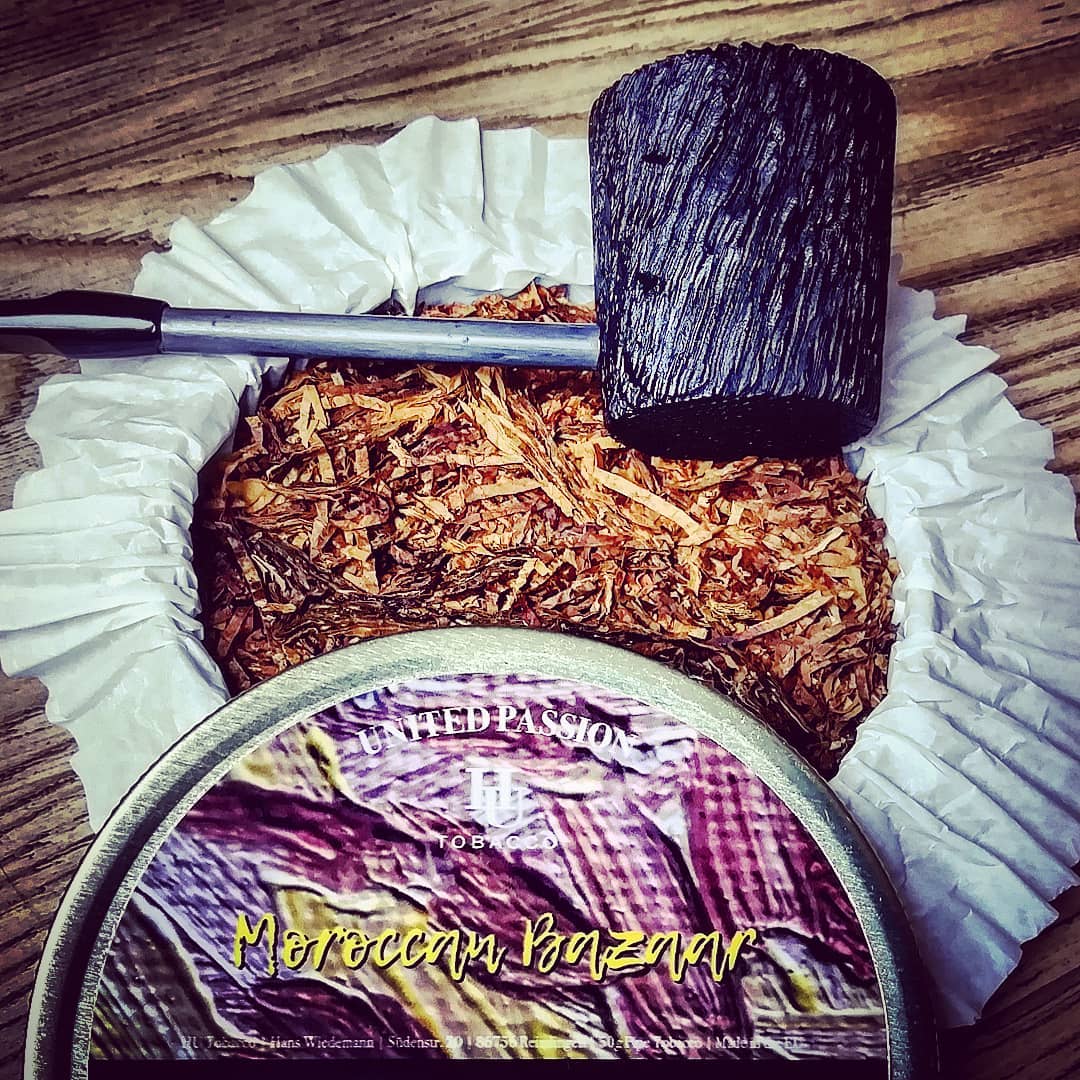
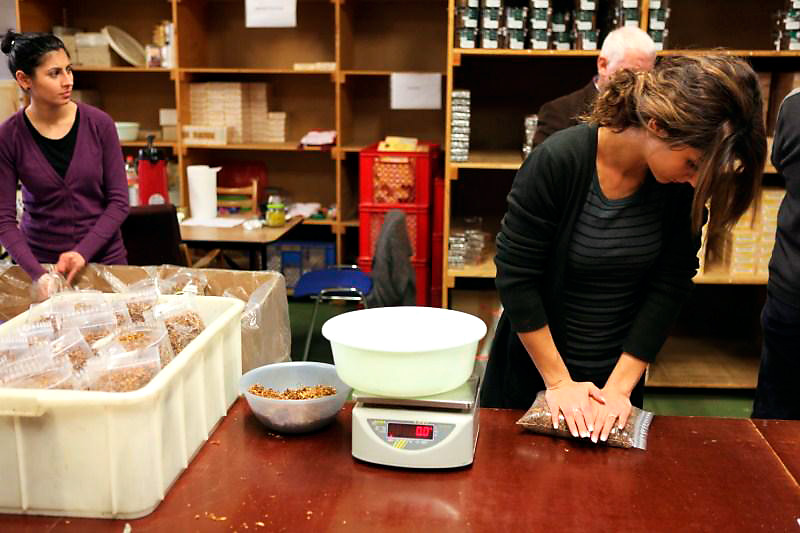
The drive there went smooth despite the whimsical weather. Which was really sad because with almost all the previous Lohmar editions it was good to excellent. We arrived pretty early which had a reason, I wanted to go to the table of HU Tobacco as fast as possible. A couple of days before Lohmar I read on the Facebook page of Hans Wiedemann (owner and master-blender of HU Tobacco) that he was releasing a special pipe-show blend. A mixture of sweet Virginias, Burley and Latakia, advertised as: Is it a Virginia blend with Latakia in the background or is it an English mixture with a pronounced Virginia sweetness? But the thing was, there were only 50 tins! I tried to reserve a tin on Facebook and crossed my fingers. When I had finally reached Hans through the vast crowd at his table I was disappointed. All pipe-show tins were gone.. In fact, lots of Hans’ blends were already sold out! Especially the newer ones that I wanted to try.. So besides some tins that friends had asked me to buy I ended up with Moroccan Bazaar (as a lover of the oriental spice markets I just have to try this blend) and RaiKo InBeTween (formerly known as RaiKo ChocoLat, due to German regulations).
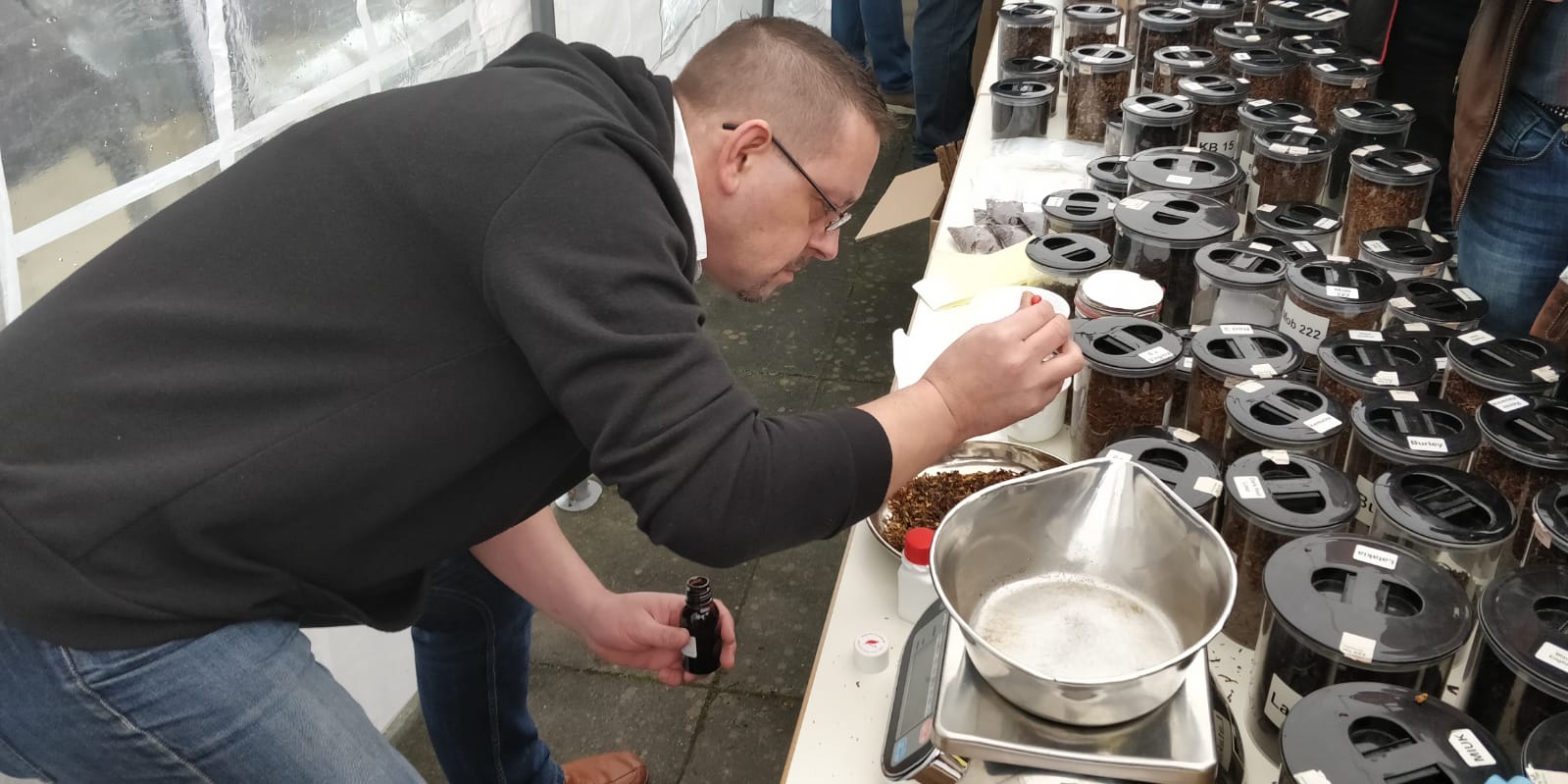
Beside the table of Hans there stood a guy with lots of jars filled with all kinds of mixing tobaccos in front of him. It was Thomas Nietsche, the master-blender of Kohlhase & Kopp. I also read on Facebook that he and Hans had put up a contest. You could create your own blend there and let it mix by Thomas. After Lohmar all the entries are smoked and the best will become the 2020 Hamm pipe-show blend plus you get a €50 HU Tobacco coupon. I know I have been not so positive about Kohlhase & Kopp in the past but I have to say this was a brilliant initiative and Thomas is a very nice bloke. While I was waiting for my turn I explained to Mark (in Dutch) the purpose of all of this. “I understood some of that!” Thomas said jokingly while blending some tobaccos. When it was my turn I had a faint idea in my head. I wanted a kind of Balkan blend with a touch of aromatics. Very tricky because Latakia does not do well with added flavours. I instructed Thomas to begin with 30% Cyprian Latakia, then 20% orientals. I asked if he had a good Red Virginia and he did have some aged one, he put in 30%. To round it off I let him add 10% Bright Virginia and 10% unsweetened Black Cavendish. I already saw that he had some small bottles with concentrated flavours so I instructed Thomas to add just a few drops of milk-chocolate and vanilla essence to the mixture. The result was a blend that at least smelled heavenly. Vanilla-like toffee with a smoky background. Thomas saved a sample for the contest (entry no. 7 on the list) and the rest was given free of charge to me.
Because of the bad weather it was crazily busy in the tents where a lot of the exhibitors showed their wares. I opted to go to the villa itself, still crowded, but more space to manoeuvre. Almost immediately I bumped into Rudi, Fred and Paul. Especially the last one I had not seen in quite a while. After talking a little bit we discovered we were in the way so I went along. There are many skilled pipe-makers at Lohmar but often the prices they ask.. Woww.. So I was pleasant surprised when I saw a pipe I wanted for a fair sum made by Berlin based Lucifer’s Pipe. It was a nicely shaped duke made of morta. Since I always wanted a pipe made of the dark wood I did not have to think long of buying it. I even got a discount without asking for it! When I turned around a gentleman approached me. “Hello Arno do you remember me?” Although his face was vaguely familiar I could not remember him. “I am Hans-Walter, we met here some years ago, there is a picture of me on your blog. Which I love by the way! The history of for example De Graaff or Capstan blends is what interests me.” Some wheels turned in my head and suddenly I remembered him. If you read this, Hans-Walter, sorry I did not recognize you immediately! I meet so many people… And thanks for your kind words! Hope you will come to Hamm next year.
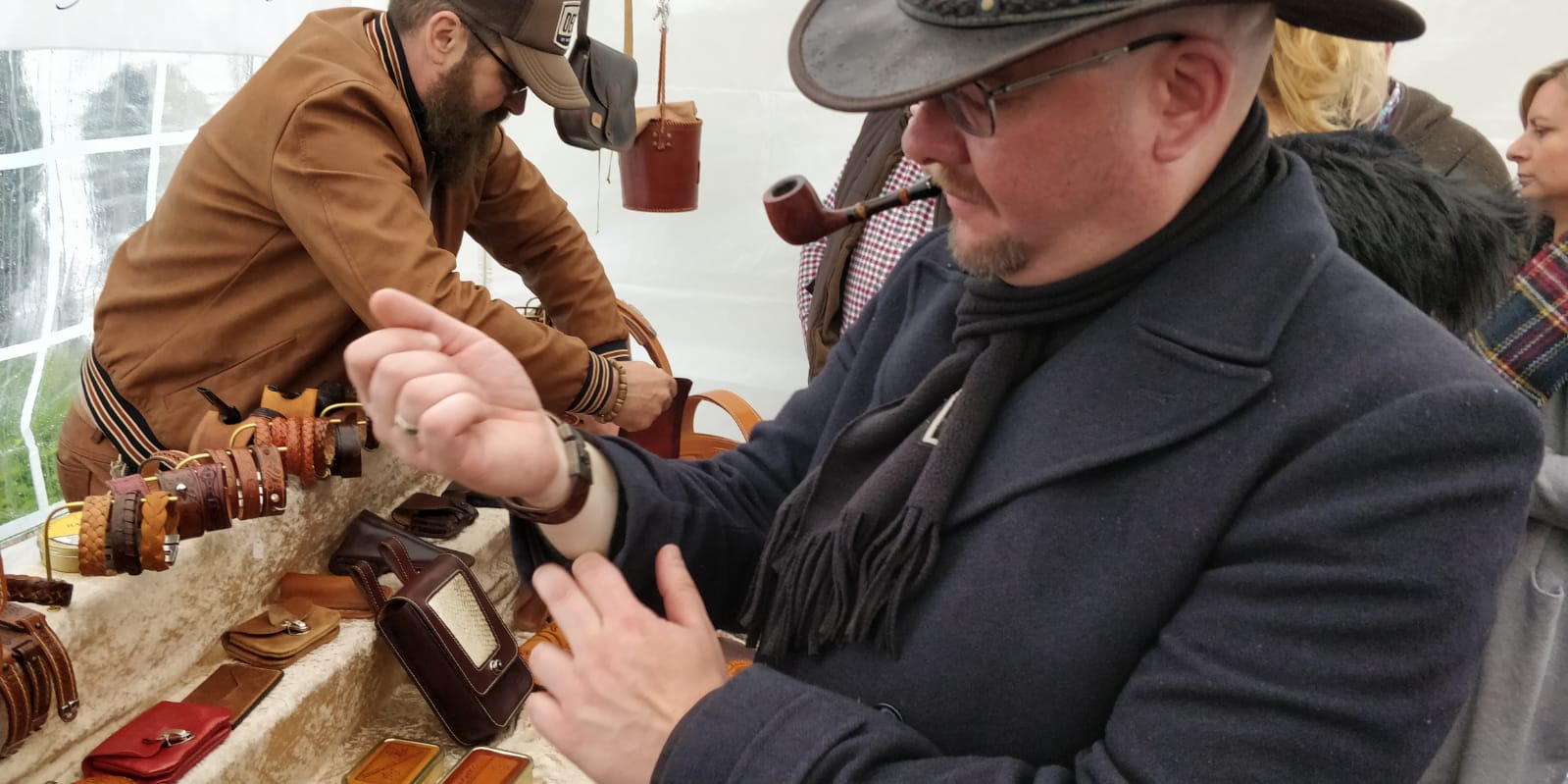
Back in one of the tents I decided to pay a visit to Adrian. Every year he is there with his hand-made leather wares and is he a very nice chap. I always have to think a bit of Blackbeard the pirate when I see him. Well, actually I see him sometimes that way because Adrian loves to celebrate the carnival dressed up as a pirate in his home city of Cologne and puts pictures of it on Facebook. After talking a bit to him I took a look at his leather stuff and spotted a cool bracelet I liked. I fitted it and yes, I wanted to buy it. The price was a tad high but with my inborn Dutch skills I haggled it down. Mark also succeeded in that while buying a pipe at another stand, not my kind of pipe but really something Mark would go for. It is good we don’t all have the same taste.
Mark and I almost wanted to go (the weather got worse and worse) when we bumped into some Belgian pipe-smokers forum members: Geoff, Paul and his wife. We told them we were heading to Peter Heinrichs in Bergheim for a smoke in their pipe-museum/smoking lounge and maybe something to buy. The more the merrier so the Belgians agreed to join us. On the way really everything that could fall from the sky (except aeroplanes) hit us. Snow, rain, hail.. Blah.. When we arrived we were greeted by the widow of Peter Heinrichs (who is in charge together with her lovely daughters). I must say the old lady has an iron memory. Once I had mentioned I liked estate pipes, especially vintage Dunhills. So she produced some cases with in them old Dunhills, Charatans, Ashtons and more. I face-palmed myself because I knew this was going to cost me money. Lucky for my wallet there was no Dunhill that really took my fancy. But I did like an Ashton Pebble Grain Zulu like shape, which I bought. I also purchased a tin of Château Henri No. 24; Latakia from Syria (although I beg to differ…) and Cyprus, Virginia, a bit of Burley, orientals and Java-tobacco. In the smoking lounge I could not resist smoking the Lohmar No. 7. It was way to freshly mixed but despite that, not bad, not bad at all!
At 4 o’clock Heinrichs closed. I wanted to do some shopping at the German Lidl in Bergheim and afterwards get some dinner. The rest agreed and went with me. I just love to go to the Lidl in Germany. They have many products that we in The Netherlands do not have, they are cheaper and of better quality! Almost every time I am in Bergheim, regardless of whom I am with, I go to Dönerburger for dinner. It is a Turkish style take-away restaurant where you can also just sit and eat. Nothing fancy but the quality of their food is excellent and cheap. I repeat, cheap! That always makes this greedy Dutchman happy. I had a big plate of Döner kebab (lamb meat, I also had the choice to go for chicken) with fries, tzatziki sauce and a cola and I had to pay exactly €10! In The Netherlands you can’t go out and eat like that for that price.
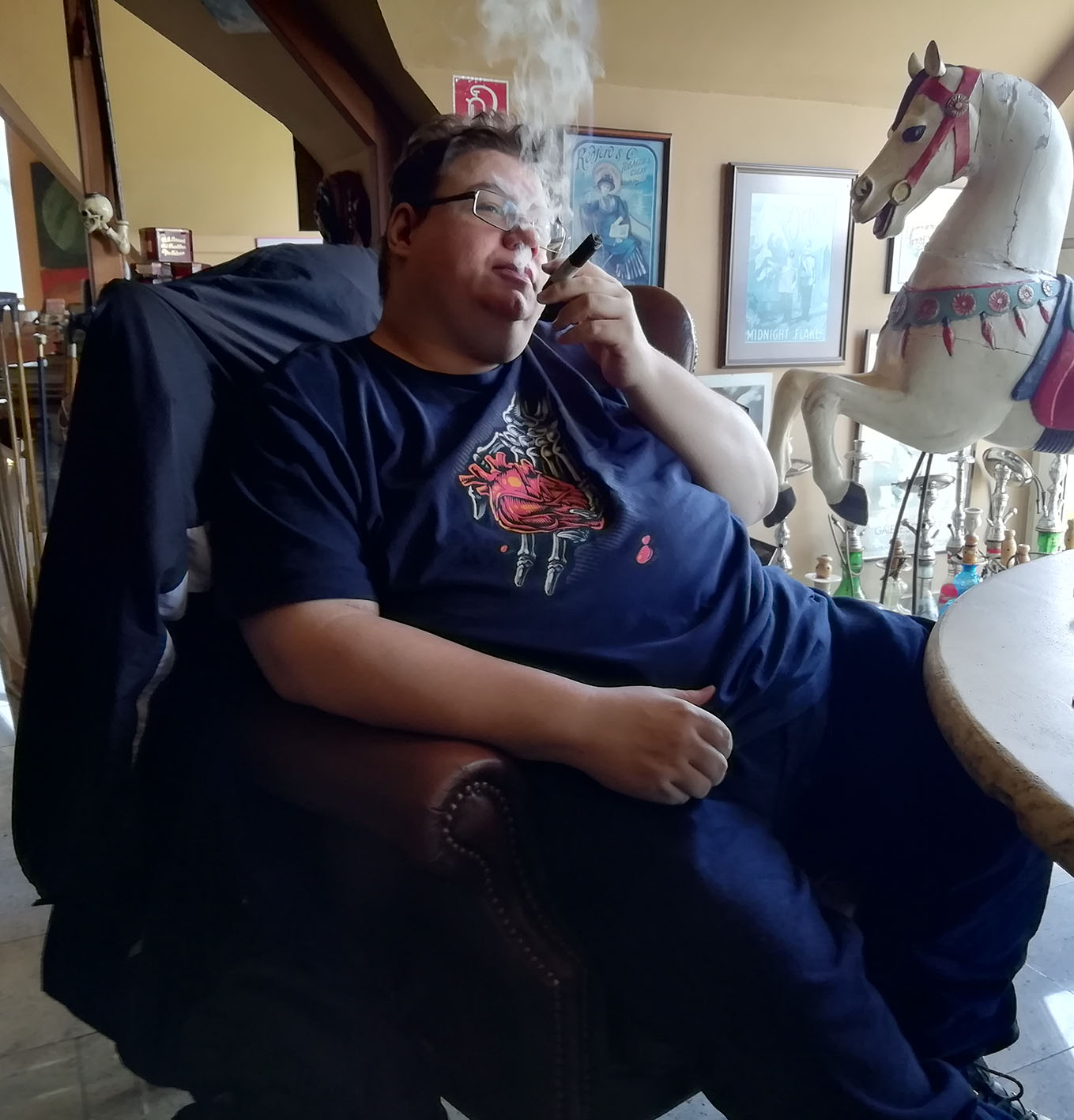
To round off the day I proposed a visit to the Rauch Lounge in the German town of Wassenberg. I had never been there and since it was more or less situated on the way home (also for the Belgians) we decided to go there. Inside we immediately bumped again into Rudi, Paul and Fred. They had gone there directly from Lohmar. Very nice because now I had the chance to talk to them a bit longer. Rauch Lounge has not been active for long, since November 2015. I must say, kudos to them, starting a tobacco shop in these anti-tobacco times. The store is loaded with all kinds of pipes, tobacco, spirits and cigars. And the best thing, they have a modern smoking lounge which is open late. It was bigger than I had imagined looking at the pictures on their site. Mark and I picked out some cigars in the humidor and together with the Belgians we sat down and smoked. The day had been perfect, a fitting goodbye to the Lohmar pipe-show.
I would like to thank Volker Bier for organising all those excellent editions of the Lohmarer Pfeifenmesse, I will remember them fondly and hope to create new memories next year in Hamm. Further thanks go out to the convivial Belgian delegation, always nice and educational to talk to them and of course Mark, who had to endure my music and farts in the car. Sorry man! All pictures (except the © ones) were made by Mark and myself.